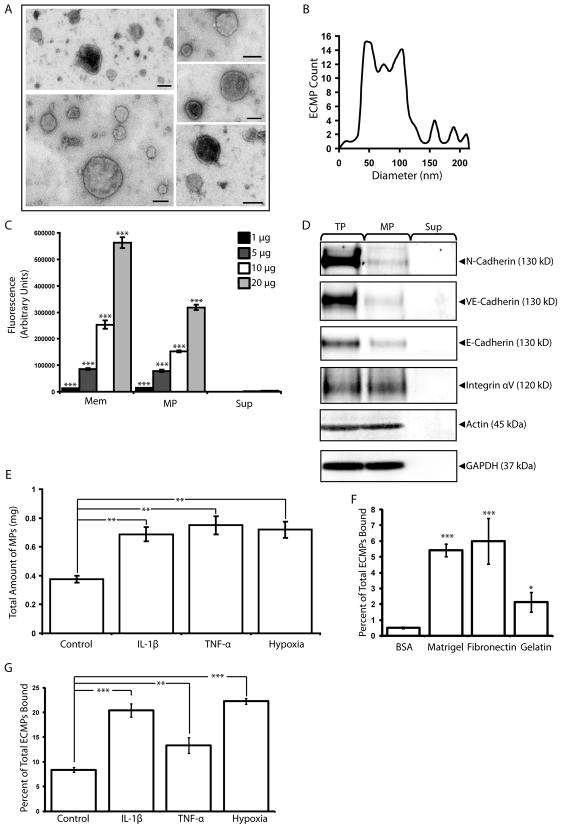
Figure 1.
MicroEC MPs are plasma membrane derived and bind to extracellular matrix substrates. (A) MPs isolated from microECs were observed by negative staining and transmission electron microscopy as intact membranous structures. (B) Size profile of isolated MPs. (C) Fluorescence photometry analysis of membranes (Mem), MP, and Sup samples (1, 5, 10, or 20 μg) isolated from DiO-labeled microECs. MPs and Mem samples were enriched for DiO. *** p < 0.001 compared to Sup values of corresponding protein amounts (D) Western blot analysis comparing localization of membrane proteins (N-cadherin, VE-cadherin, E-cadherin, Integrin αV) among microEC total protein (TP), MPs, and Sup fractions. Blots of actin and GAPDH were included as loading controls. (E) Comparison of the amount of MPs produced under control conditions or in the presence of IL-1β, TNF-α, or hypoxia. ** p < 0.01 (F) DiO-labeled MPs bound to surfaces coated with Matrigel, fibronectin, or gelatin. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 compared to BSA controls (G) Higher percentages of DiO-labeled MPs produced in the presence of IL-1β, TNF-α, or hypoxia bound fibronectin-coated surfaces than those produced under control conditions. ** p < 0.01 Results are means ± SD.