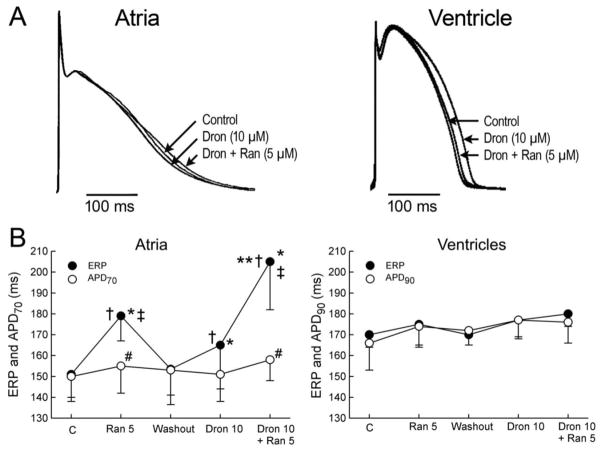
Fig. 4.
Atrial-selective induction of post-repolarization refractoriness (PRR) by ranolazine (Ran), dronedarone (Dron) alone and in combination (PRR was approximated by the difference between effective refractory period (ERP) and action potential duration measured at 70% repolarization (APD70) in atria and between ERP and APD measured at 90% repolarization (APD90) in ventricles; ERP corresponds to APD70–75 in atria and to APD90 in ventricles.
A: Shown are superimposed action potentials demonstrating relatively small changes with dronedarone and ranolazine and their combination. B: Summary data of atrial-selective induction of PRR. Ventricular data were obtained from epicardium and atrial data from endocardial pectinate muscle (PM). n=7–8. * p<0.05 vs. respective control (C). † p<0.05 vs. washout. ‡ p<0.05 vs. Dron 10. # p<0.05 vs. respective ERP. ** - p<0.05 - change in ERP induced by combination of Ran and Dron (from washout) vs. the sum of changes caused by Ran and Dron independently (both from washout). CL = 500 ms. From Burashnikov et al (Burashnikov et al., 2010a)