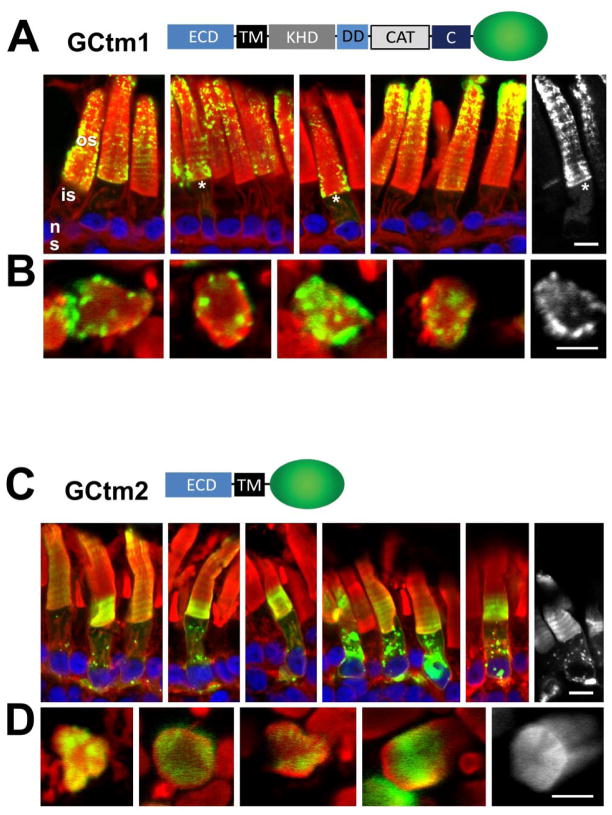
Fig. 2.
Correct targeting of GC1 requires its cytoplasmic domain. A, GCtm1 containing the entire GC1 coding sequence. GCtm1 predominantly targets to the outer segments although faint EGFP fluorescence is present in the inner segments of some rods (*). GC1-EGFP fluorescence has a particulate appearance in the outer segments, but appears uniformly distributed in inner segment endomembranes. B, Cross-sections of GCtm1 show localization to the edges of disc membranes. C, GCtm2 containing the entire extracellular domain of GC1 including TM. The ECD-EGFP fusion protein distributes among membranes of the outer segment, inner segment and synaptic terminals. D, Cross-sections of GCtm2. While not targeting correctly, the GCtm2 fusions protein locates diffusely to the disc edges. The distribution of GCtm1 suggests correct targeting although overexpression or fusion to EGFP may cause the fusion protein to misfold and accumulate in the ER. In contrast, the diffuse localization of GCtm2 suggests that targeting information is absent. Green, EGFP fluorescence; red, Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin; blue, Hoechst 33342. Scale bars: 10uM.