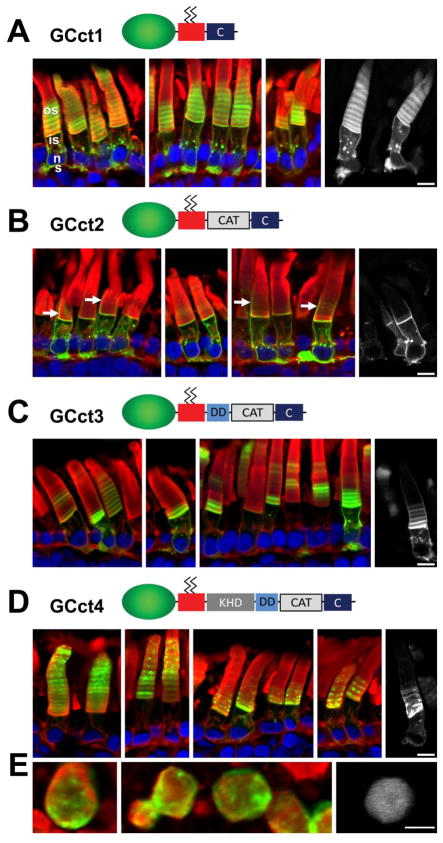
Fig. 5.
The cytoplasmic region of GC1 can direct outer segment targeting of a membrane-associated fusion protein. A, GCct1 containing the distal C-terminal 83 amino acids of GC1. GCct1 is present in outer segment, inner segment and synaptic membranes. B, GCct2 containing the distal C-terminus and the catalytic domain. GCct2 is found primarily in the inner segment endomembranes, plasma membrane, the calycal processes (white arrows), and synaptic terminals. Interestingly, the GCct2 fusion protein appears significantly excluded from outer segments. C, GCct3 containing DD, CAT and C-term. GCct3 is present in outer segment, inner segment and synaptic membranes. In contrast to GCct2, GCct3 is not excluded from the OS. D, GCct4 containing the entire GC1 cytoplasmic domain. As seen for the full-length GC1 fusion protein (GCtm1, Fig. 2A), GCct4 traffics almost exclusively to the OS. Inner segments reveal only faint EGFP fluorescence in an ER-like distribution. E, cross-sections of GCct4 (left and middle) showing tendence of GCct4 to segregate to disc edges. Green, EGFP fluorescence; red, Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin; blue, Hoechst 33342. Scale bars: 10uM.