Abstract
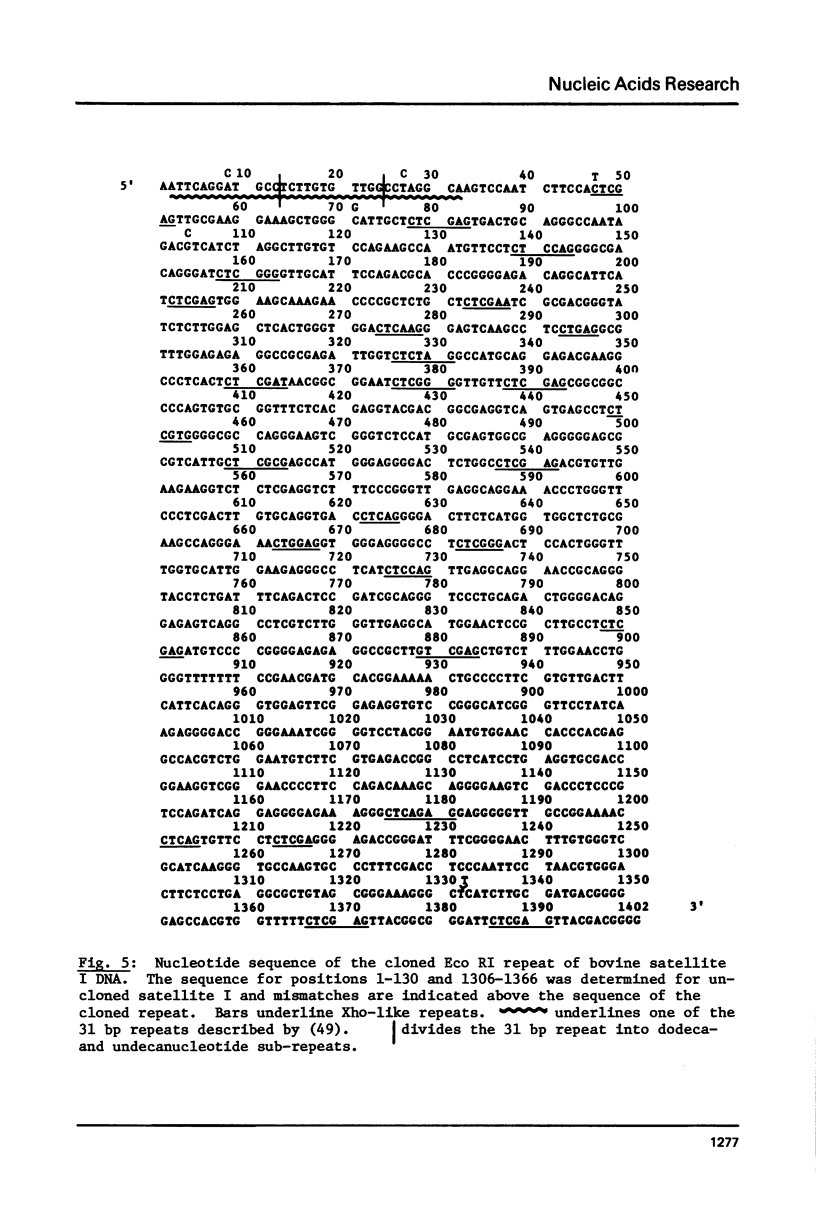
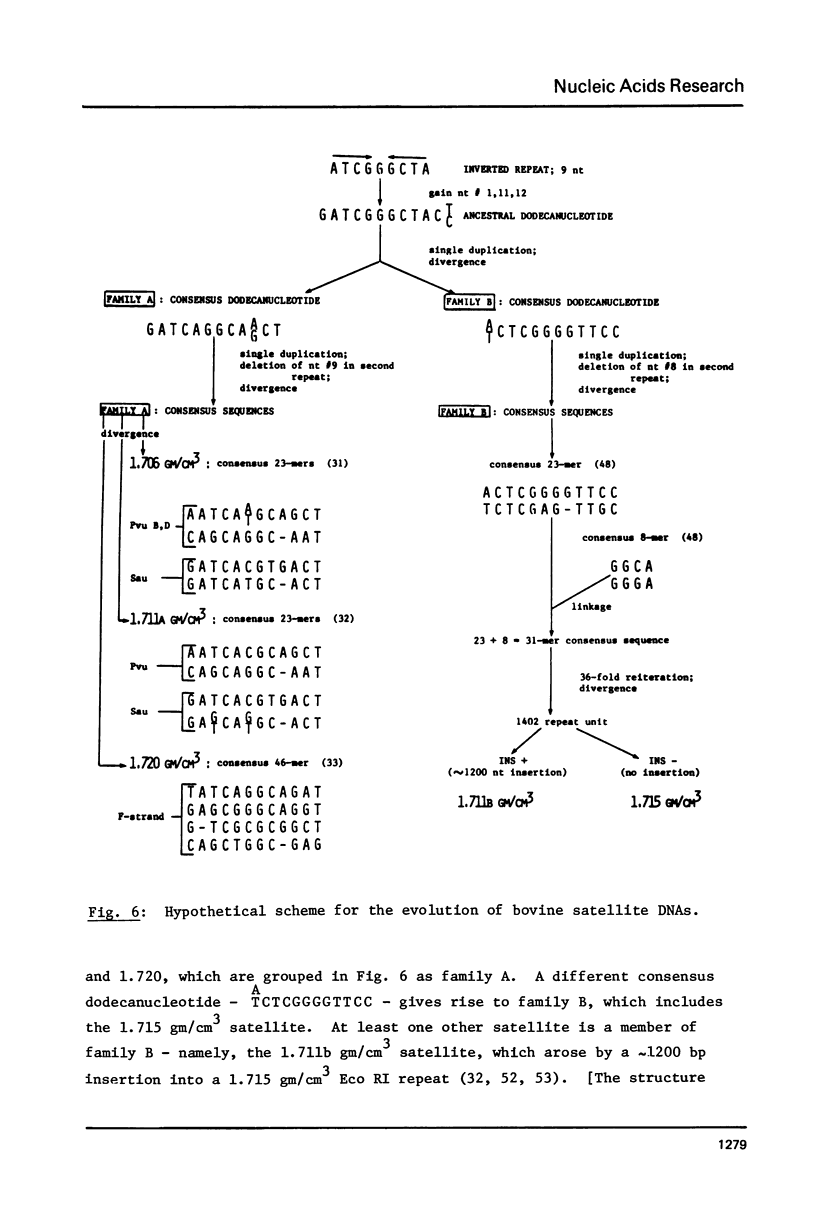
The 1402 bp Eco RI repeating unit of bovine satellite I DNA (rho CsCl = 1.715 gm/cm3) has been cloned in pBR322. The sequence of this cloned repeat has been determined and is greater than 97% homologous to the sequence reported for another clone of satellite I (48) and for uncloned satellite I DNA (49). The internal sequence structure of the Eco RI repeat contains imperfect direct and inverted repeats of a variety of lengths and frequencies. The most outstanding repeat structures center on the hexanucleotide CTCGAG which, at a stringency of greater than 80% sequence homology, occurs at 26 locations within the RI repeat. Two of these 6 bp units are found within the 31 bp consensus sequence of a repeating structure which spans the entire length of the 1402 bp repeat (49). The 31 bp consensus sequence contains an internal dodecanucleotide repeat, as do the consensus sequences of the repeat units determined for 3 other bovine satellite DNAs (rho CsCl = 1.706, 1.711a, 1.720 gm/cm3). Based on this evidence, we present a model for the evolutionary relationship between satellite I and the other bovine satellites.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botchan M. R. Bovine satellite I DNA consists of repetitive units 1,400 base pairs in length. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):288–292. doi: 10.1038/251288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D., Carlson M., Fry K., Hsieh T. S. DNA sequence organization in Drosophila heterochromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1137–1146. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Brutlag D. Cloning and characterization of a complex satellite DNA from Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers C. A., Schell M. P., Skinner D. M. The primary sequence of a crustacean satellite DNA containing a family of repeats. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corneo G., Ginelli E., Polli E. Different satellite deoxyribonucleic acids of guinea pig and ox. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1565–1571. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L., Furlong C., Gillespie D., Kurnit D. DNA sequence of baboon highly repeated DNA: evidence for evolution by nonrandom unequal crossovers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2129–2133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A. Analysis of Drosophila melanogaster satellite IV with restriction endonuclease MboII. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Polan M. L., Gall J. G. Satellite DNA sequences of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):665–692. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
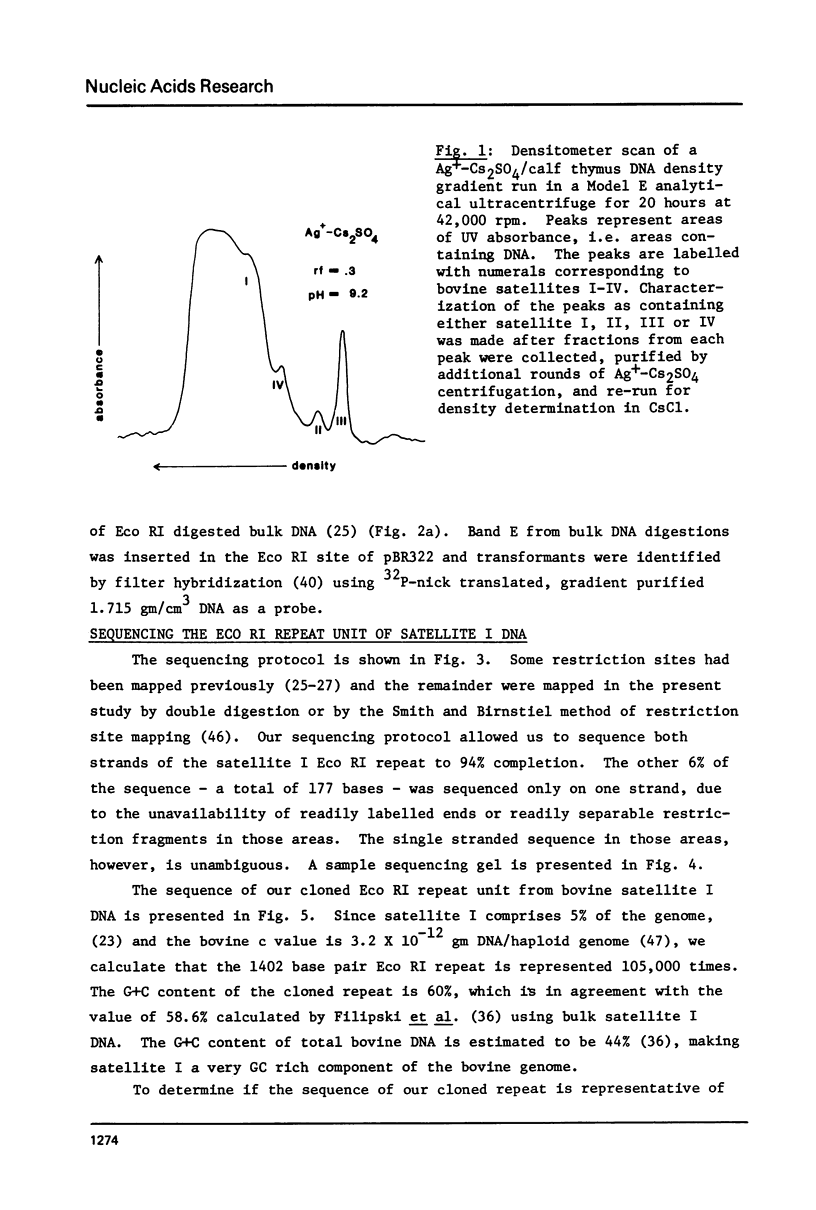
- Filipski J., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by Cs2SO4-Ag density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):177–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry K., Brutlag D. Detection and resolution of closely related satellite DNA sequences by molecular cloning. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):581–593. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Doly J., Cortadas J., Bernardi G. The primary structure of bovine satellite 1.715. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6069–6082. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Atherton D. D. Satellite DNA sequences in Drosophila virilis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):633–664. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Cohen E. H., Atherton D. D. The satellite DNAs of Drosophila virilis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:417–421. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Gerbi S. A. Fine structure of ribosomal RNA. IV. Extraordinary evolutionary conservation in sequences that flank introns in rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3623–3637. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Nucleotide sequence of mouse satellite DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):683–696. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecka H., Macaya G., Cortadas J., Thiéry J. P., Bernardi G. Restriction enzyme analysis of satellite DNA components from the bovine genome. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Furtak K., Szymczak G., Bartnik E., Skowroński J., Panusz H. Molecular cloning of the restriction fragments derived from double EcoRI/PstI digestion of the calf satellite I DNA and their restriction analysis. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 Dec;34(12):1151–1155. doi: 10.1515/znc-1979-1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya G., Cortadas J., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by density-gradient centrifugation. Preparation of the dG+dC-rich DNA components. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Consensus sequence of mouse satellite DNA indicates it is derived from tandem 116 basepair repeats. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):25–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80746-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray S. L., Gerbi S. A., Landy A. Interdigitated repeated sequences in bovine satellite DNA. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):367–370. doi: 10.1038/253367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Blumenfeld M. Satellite Ic: a possible link between the satellite DNAs of D. virilis and D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. Patchwork structure of a bovine satellite DNA. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):883–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. Investigation of the repetitive sequences in calf DNA by cleavage with restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):55–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöschl E., Streeck R. E. Prototype sequence of bovine 1.720 satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizes G. A possible structure for calf satellite DNA I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2677–2696. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Deininger P. L., Houck C. M., Schmid C. W. A dimer satellite sequence in bonnet monkey DNA consists of distinct monomer subunits. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 15;136(2):151–167. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Biro P. A. Sequence and evolution of mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):357–374. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E. Inserted sequences in bovine satellite DNA's. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):443–445. doi: 10.1126/science.6264600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. A long-range and two short-range periodicities are superimposed in the 1.706-g/cm3 satellite DNA from calf thymus. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):267–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]