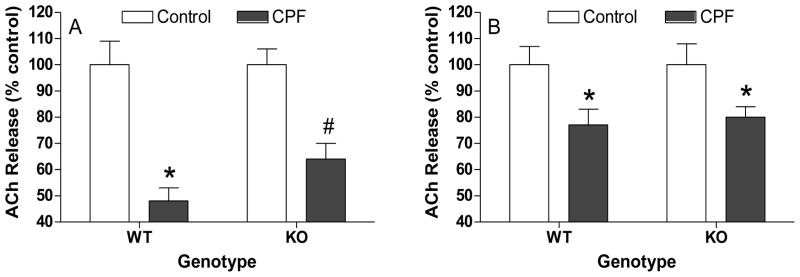
Figure 4. Effects of chlorpyrifos on ACh release ex vivo in hippocampal and striatal slices from wild type (WT) and CB1 knockout (KO) mice.
Mice (n = 5–6/group) were exposed to either vehicle or chlorpyrifos and sacrificed 48 h later. Hippocampal (A) and striatal (B) slices were incubated with [3H]choline to label endogenous acetylcholine. Prelabelled slices were then loaded into a suprafusion apparatus and perfused with physiological buffer. Release was stimulated by exposing the slices to buffer containing a high concentration of KCl (25 mM for hippocampus; 20 mM for striatum) as described in Methods. Data (mean ± standard error) represent depolarization-induced ACh release (S1) and are expressed as percent of control values. An asterisk indicates a significant difference compared to respective controls while a pound sign indicates a significant difference in release between tissues from wild type and CB1 knockout mice.