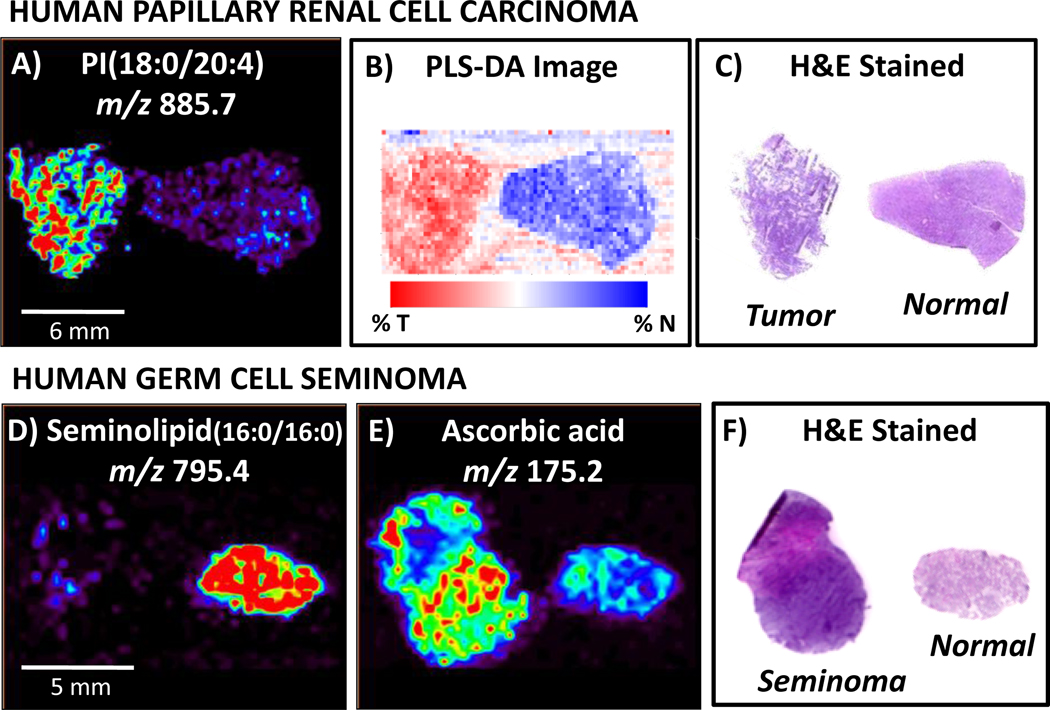
Fig. 9.
DESI-MS imaging has been used to analyze human cancerous tissue, including human papillary renal cell carcinoma and human germ cell seminoma. Agreement is seen between A) DESI-MS ion image of m/z 885.7, identified as PI(18:0/20:4), B) PLS-DA synthetic image using all ions and C) H&E stained tissue sections, enabling cancer diagnosis. Human germ cell tissue analysis by DESI imaging revealed hat D), while seminolipid (16:0/16:0), m/z 795.4, occurs in abundance in normal tubules, E)ascorbic acid, m/z 175.2, was present at higher intensities in cancerous tissue. This distinction between cancerous and normal germ tissue is consistent with F) diagnosis obtained from pathological analysis of H&E stained tissue sections. Adapted from references 4 and 55