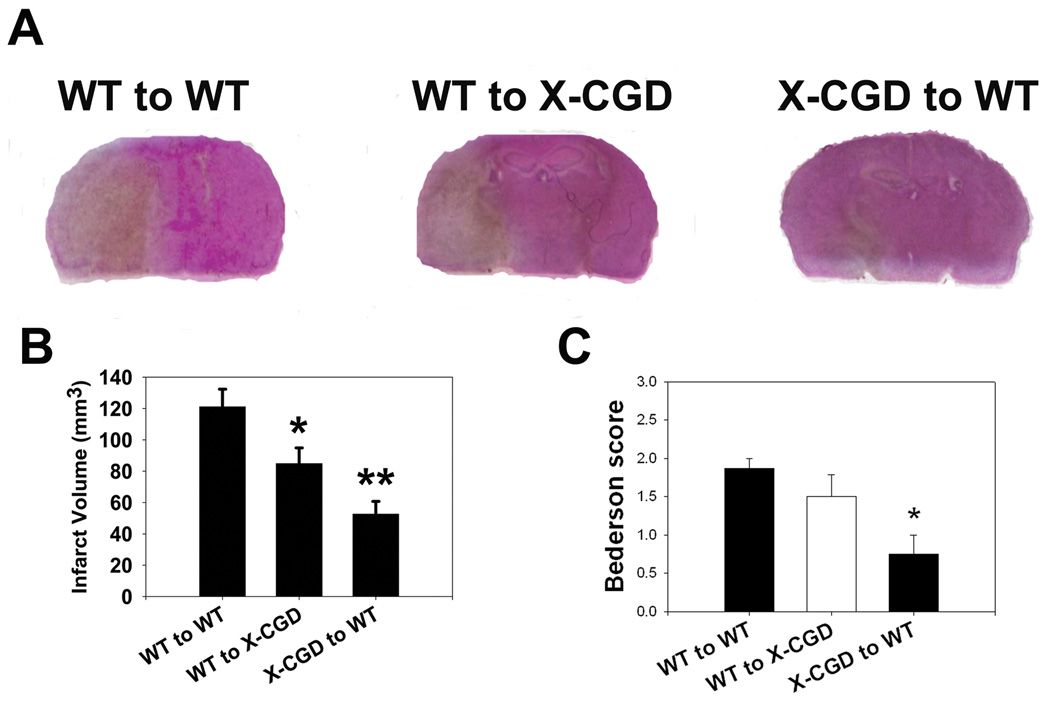
Fig. 4. Marrow derived NOX2 contributes more to brain ischemia than brain derived NOX2.
Wildtype (WT) mice receiving NOX2 deficient marrow (X-CGD to WT) and NOX2 deficient mice receiving WT marrow (WT to X-CGD) both had smaller infarcts than WT mice receiving WT marrow (WT to WT) (A, B). However, X-CGD to WT chimeras have even smaller infarcts than WT to X-CGD chimeras indicating that NOX2 generated in the circulating marrow derived cells contributes to ischemic damage more than NOX2 in the brain. Bederson scores indicate that X-CGD to WT chimeras had better neurological function compared to both WT to WT and WT to X-CGD chimeras (C). (n=6/group, *P<0.05 vs. WT to WT, **P<0.05 vs. WT to WT and WT to X-CGD)