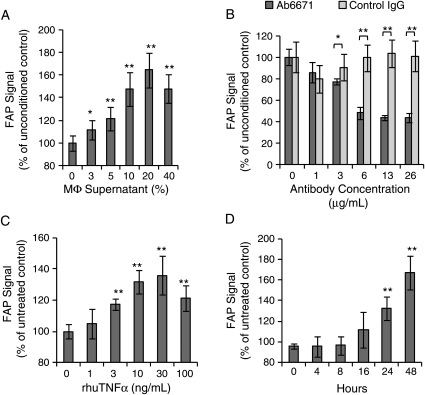
Figure 6.
Macrophage-derived tumour necrosis factor α induces fibroblast activation protein expression in human aortic smooth muscle cells. (A) Macrophage-conditioned supernatant induces fibroblast activation protein in human aortic smooth muscle cells in a concentration-dependent manner following 48 h exposure (n = 6). (B) Using the same macrophage-conditioned medium, tumour necrosis factor α-blocking antibody (Ab6671) decreases fibroblast activation protein expression by 40% in human aortic smooth muscle cells compared with an isotype control antibody (n = 6). (C) Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor α induces fibroblast activation protein in human aortic smooth muscle cells in a dose-dependent manner after 48 h incubation (n = 6). (D) Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor α induces fibroblast activation protein in human aortic smooth muscle cells in a time-dependent manner (30 ng/mL). AU, arbitrary units (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).