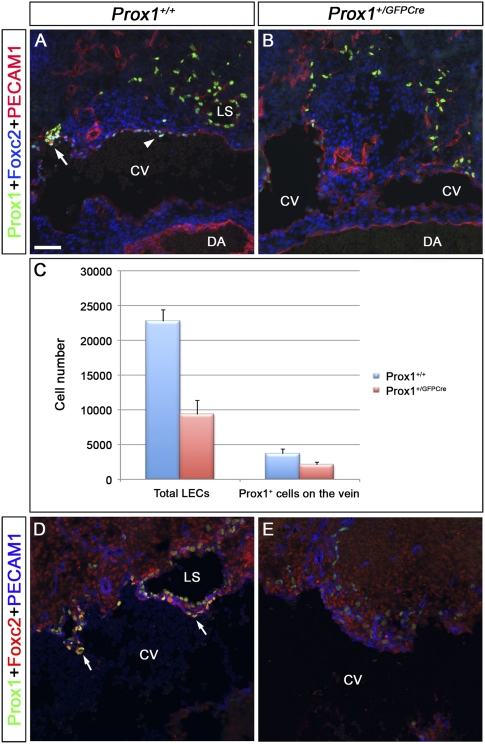
Figure 4.
The number of Prox1-expressing LEC progenitors and Prox1-expressing venous ECs that will form the lymphovenous valves is reduced in Prox1 heterozygous embryos. (A,B) E11.5 control (A) and Prox1+/GFPCre (B) embryos were frontally sectioned and immunostained for Prox1, Foxc2, and PECAM1. (A) In the control embryos, Foxc2 is weakly expressed in the Prox1+ cells on the vein (arrowhead). In addition, lymph sacs and occasionally one valve rudiment (arrow) could be observed. (B) In Prox1+/GFPCre embryos, the total number of LECs appears to be reduced, and no lymph sacs or valve rudiments are seen. (C) Compared with wild-type littermates, the total number of Prox1+ PECAM1+ ECs on the vein and outside the vein were reduced in E11.5 Prox1+/GFPCre embryos (n = 3 for each genotype, P < 0.05). (D,E) E12.5 control (D) and Prox1+/GFPCre (E) embryos were frontally sectioned and immunostained for Prox1, Foxc2, and PECAM1. (D) In control embryos, Foxc2 is expressed on the valve rudiments (arrows), which lie adjacent to the primitive lymph sacs. (E) In Prox1+/GFPCre embryos, the total number of LECs appears to be reduced, and no valve rudiments are seen. Lymph sacs are also not observed in this location. The head is oriented toward the right, the heart is oriented toward the left, and the thymus is oriented toward the bottom in all panels. (CV) Cardinal vein; (DA) dorsal aorta; (LS) lymph sac. Bar, 50 μm.