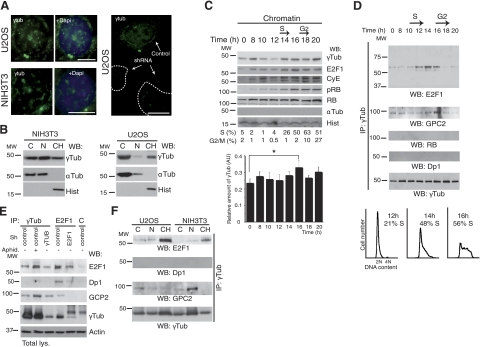
Figure 1.
γ-Tubulin localizes to chromatin and interacts with E2F1. A) Localization of endogenous γ-tubulin (eγTub) was examined by immunofluorescence staining with γTub (green), and nuclei were detected with DAPI (blue) in NIH3T3 and U2OS cells expressing human γ-TUBULIN -shRNA. Scale bars = 10 μm. B) Cells (0.5×106) were biochemically divided into cytosolic (C), nuclear (N), and chromatin (CH) fractions and analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with an anti-γ-tubulin antibody (γTub), α-tubulin (αTub) and histone (Hist) (n=5 or 6). C) Extracts from synchronous NIH3T3 cells were prepared as in A and examined by WB using antibodies against E2F1, cyclin E (CyE), phosphoretinoblastoma (pRB), total RB, γ- and α-tubulin, and histone (n=6). DNA content was determined by flow cytometry (percentage of S- or G2/M-phase cells, indicated beneath blots). Graph illustrates densitometric analysis of γTub content in the chromatin fraction (means±sd; n=6). *P < 0.05. D) Using extracts from synchronous NIH3T3 cells, γ-tubulin was immunoprecipitated with an anti-γ-tubulin antibody, developed by WB with an anti-E2F1 antibody (top), and reprobed with GCP2, RB, Dp1, and γTub (bottom). Bottom panels illustrate DNA content of the cells detected by flow cytometry (percentage S-phase cells indicated, n=5). E) Immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies or with a control antibody (C) was performed using U2OS cells expressing human γ-TUBULIN- or E2F1-shRNA, or control plasmids. Some control cells were treated with aphidicolin (Aphid.). Total lysate was run as loading control (bottom panel; n=4), and WBs were analyzed with the indicated antibodies. F) NIH3T3 and U2OS cells were biochemically divided into cytosolic, nuclear membrane, and chromatin fractions. Each fraction was subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-γ-tubulin antibody and examined by WB.