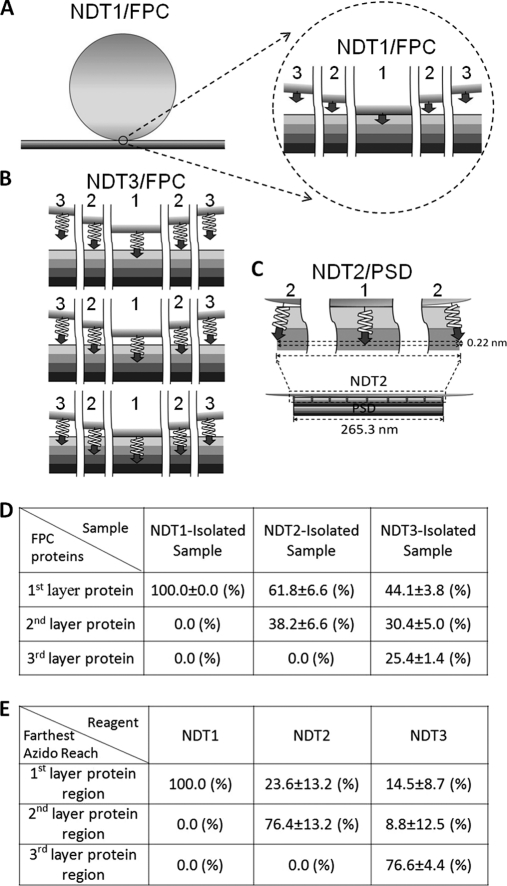
Fig. 3.
Modes of interaction of NDT reagents with FPC and PSD. A, The interaction between NDT1 and FPC. The NDT1 is depicted as a sphere sitting on top of FPC, as four consecutive planar layers in different shades. The portion enclosed by the circle is shown at higher magnification to the right. Position 1 indicates the region of NDT1 surface where the azido group of SAED ([GRAPHIC]) reaches farthest, 3.44 nm, in FPC. Positions 2 and 3 indicate respectively the regions 537 nm and 770 nm horizontally away from the position 1 on the bead surface. B, Three modes of interaction between NDT3 and FPC. Top, middle, and bottom rows: The interaction mode that the farthest depth where azido group of the 20-mer peptidyl-SAED ([GRAPHIC]) penetrates is in the first, second, and third protein layer region, respectively. In each of these interaction modes, position 1 indicates the region of the bead where the azido groups reach farthest into the FPC, and positions 2 and 3 respectively indicate the azido groups in areas 537 nm and 770 nm horizontally away from position 1 on the bead surface. C, The interaction between NDT2 and PSD. Bottom panel: The azido groups in the center region of NDT2 reach into the PSD structure, depicted as a multilayered structure of 265.3 nm wide at the bottom, to a depth similar to its spacer's length, 7.2 nm. Top panels: Enlarged views of the azido groups in the center region (position 1) and azido groups in areas on the bead surface 133 nm horizontally away from position 1 (position 2). The difference in the depths where the azido groups in regions depicted in positions 1 and 2 reside has been calculated to be 0.22 nm. D, Quantification of the abundances of the proteins in different layers of the FPC in the NDT1-, NDT2-, and NDT3-isolated samples from the densitometric scans of the gels (Fig. 2D). Data are the means ±S.D. from three independent experiments. E, The proportions of NDT beads in different interaction modes with FPC during the UV-activated crosslinking reaction as calculated by the equations described in Materials and Methods.