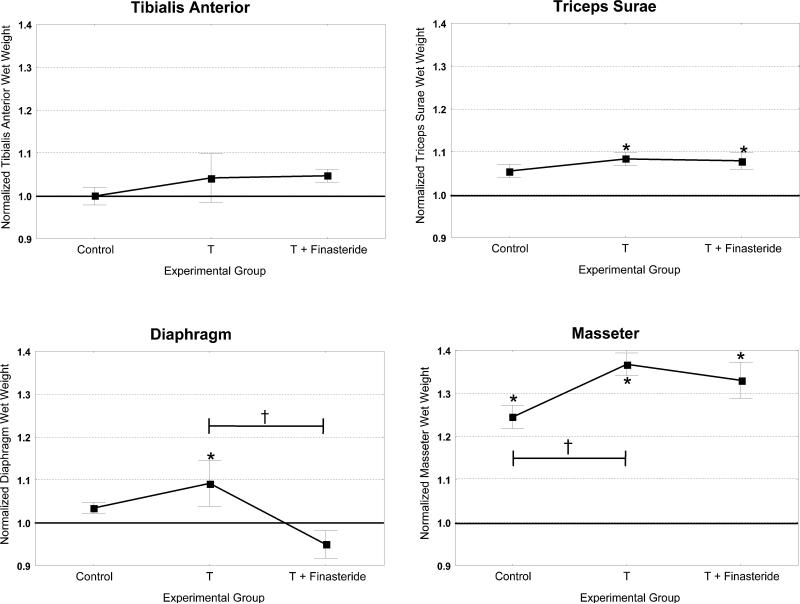
Figure 6.
Androgen responsiveness of adult limb, diaphragm and masseter muscles. CD-1 male mice at 11 weeks post-castration were supplemented for three weeks with testosterone (T) or testosterone and finasteride. Controls had no supplementation. Graphs represent wet weights of muscle from the supplementation/control groups normalized to corresponding wet weights from a parallel group of castrated animals. Significant differences in wet weights between experimental groups and castrated condition are indicated by an asterisk (*). The masseter muscle was the only one of the four muscles examined that had a significant reduction in wet weight after castration. Three muscles were found to significantly increase their wet weight after testosterone supplementation (triceps surae, diaphragm and masseter). Only diaphragm had a significant reduction with testosterone and finasteride. Significant differences between experimental groups are indicated by a † symbol (p < 0.05).