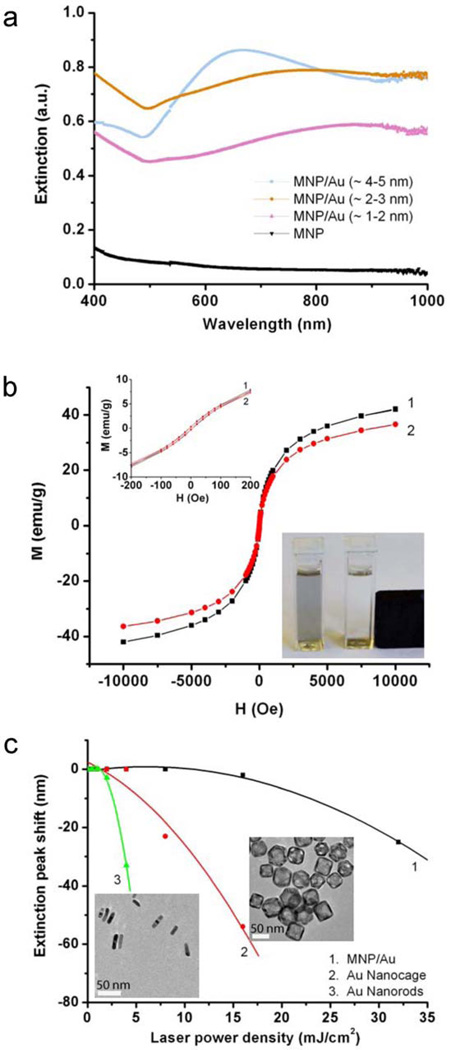
Figure 3. Optical and magnetic properties and stability of the MNP-gold hybrid NPs.
(a) Extinction spectra of MNPs successively coated with PL-PEG-COOH and PLH (black), and with gold nanoshells of various thickness, 1–2 nm (brown), 2–3 nm (purple), and 4–5 nm (red). As the gold nanoshell thickness increases, the spectral intensity increases and the peak center blue shifts. (b) Magnetization as a function of magnetic field at room temperature for MNP (black) and MNP-gold (2–3 nm shell thickness) (red). The gold shell coating has negligible effect on MNPs’ magnetic behavior. The insets show the absence of magnetic hysteresis and magnetic separation of the MNP-gold NPs. (c) Photothermal stability of the MNP-gold NPs in comparison with gold nanocages and nanorods. Extinction peak shifts as a function of laser fluence indicate that nanocages and nanorods start to quickly degrade at 5 mJ/cm2, whereas the MNP-gold hybrid NPs remain stable against laser irradiation of approximately three times higher fluence. TEM images of the nanocages and nanorods are shown as insets, scale bars are 50 and 100 nm for nanocages and nanorods, respectively.