Figure 1. Proposed model of TIM-1 signaling in activated T cells.
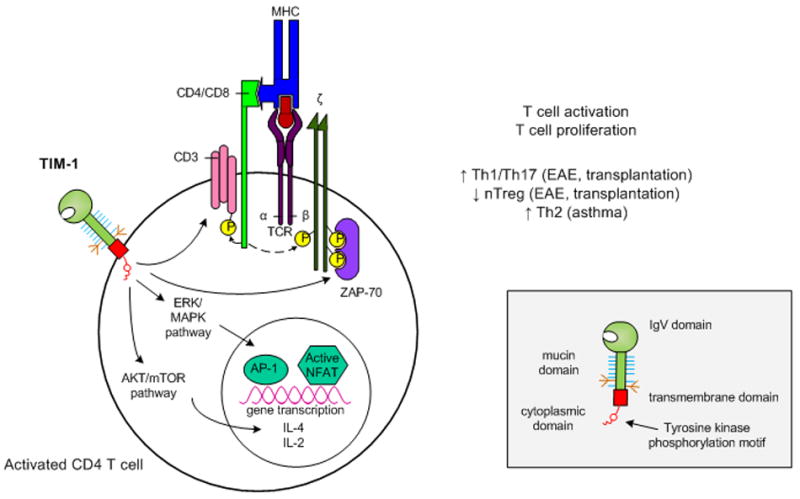
Upon ligation, tyrosine kinase residues in the TIM-1 cytoplasmic domain become phosphorylated. This leads to activation of Akt and ERK/MAPK which results in enhanced IL-2 and IL-4 transcription. In addition, TIM-1 ligation itself may be sufficient to initiate T cell activation through CD3 capping and increased phosphorylation of adaptor proteins associated with the TCR complex. Overall, TIM-1 signaling leads to enhanced T cell activation and proliferation, but the nature of the resulting T helper cell differentiation appears to be dependent on the susceptibility of the model system studied.
Inset: Domain structure of a TIM family member.
TIM members are composed of an IgV domain, mucin domain, transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain. Additionally, TIM-1 and TIM-3 possess tyrosine kinase phosphorylation motifs within their cytoplasmic domains.
