Table 4. Features of the available tools for the analysis of coordinate and SNVs.
| Software | Time | Peak Memory Usage (MB) | Comments |
| For Coordinates | |||
| CisGenome | 12m42s | 11.2 | • Can select different ranges to consider for upstream and downstream• Single output, no statistics |
| PeakAnnotator | unknown |
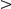 33000 33000 |
The program exceeded the available RAM on our server |
| Segtor | 5m48s | 842 | • Multiple fixed ranges for upstream and downstream• Various files depending on the biological question |
| For SNVs | |||
| SeqAnt | 63m11s | 805 | • Cannot specify a range parameter for upstream/downstream• Limited number of species |
| Annovar | 3m18s | 228 | • Fast and memory efficient• Does not provide statistics, reports a single isoform per hit |
| Sequence Variant Analyzer | 120m50s | 7700 | • Graphical User Interface• Provides greater information at the expense of speed |
| Segtor | 8m58s | 1579 | • Produces output files and statistics on a per hit, per gene or per isoform basis• Can produce the set of mutated protein sequences |
A case study of using the currently available software tools for annotating SNVs and coordinates to characterize genomic position of the 2,707,221 SNVs from the SRX016474 dataset. The corresponding coordinates of the SNVs were used as inputs for the software aimed at annotating coordinates. With the exception of Sequence Variant Analyzer which came with its own pre-compiled set of various gene databases, every tool in the list used RefSeq as source of annotation. These tests were conducted on an server with 8 CPUs at 2.5 GHz and 33 GB of RAM.
