FIGURE 7.
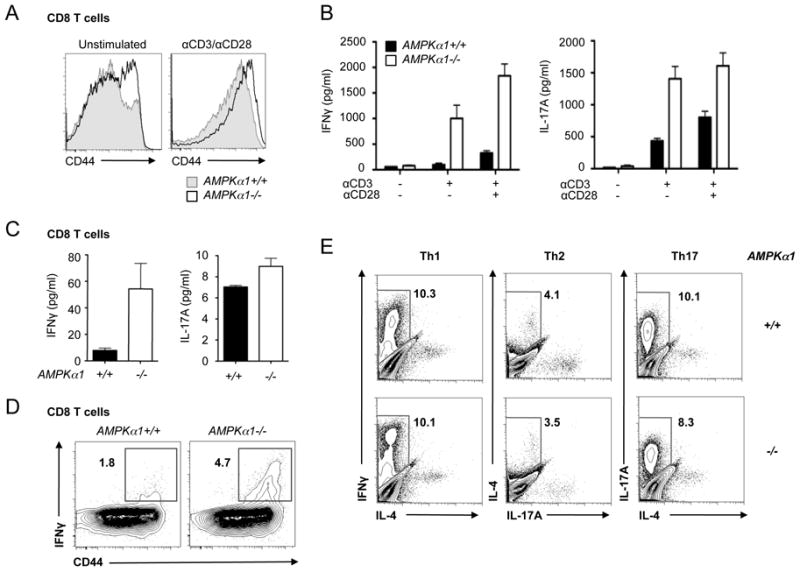
Loss of AMPKα1 promotes hyperactivation of CD8+ T cells. A, CD44 surface expression on AMPKα1-deficient T cells. T cells isolated from control (grey histogram) or AMPKα1-/- (open histogram) mice were left unstimulated (left panel) or anti-CD3/CD28 treated (right panel) for 24 hours. CD44 surface expression on CD8+ T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. B, Inflammatory cytokine production by activated AMPKα1-deficient T cells. Wild type (black bars) or AMPKα1-null (open bars) T cells were activated with anti-CD3 antibodies in the presence or absence of anti-CD28 costimulation (0.5 μg/ml). Culture supernatants were harvested and analyzed for IFN-γ or IL-17A levels by ELISA. C, IFN-γ (left panel) and IL-17A (right panel) production by anti-CD3/CD28-activated CD44loCD8+ T cells from AMPKα1+/+ (black bars) or AMPKα1-/- (open bars) mice. Cytokines were measured by ELISA 24 hours post-stimulation. D, IFN-γ production by AMPK-deficient T cells. Splenocytes from AMPKα1+/+ or AMPKα1-/- animals were activated with anti-CD3 antibodies, and IFN-γ-producing cells were identified by ICS and flow cytometry. Surface expression of CD44 versus intracellular IFN-γ is displayed for CD8+ cells. E, T helper differentiation of AMPKα1-/- T cells in vitro. AMPKα1+/+ or AMPKα1-/- CD44loCD4+ T cells were cultured in Th1, Th2, or Th17 skewing conditions and examined for effector function after 4 days of culture by intracellular staining for IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-17.
