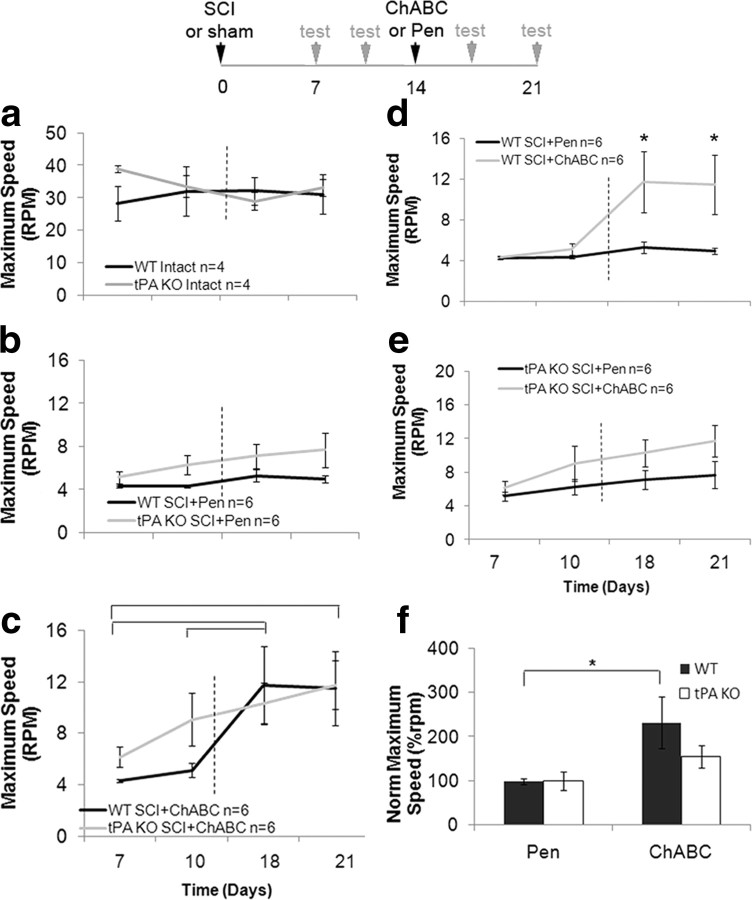
Figure 6.
ChABC promoted motor balance is attenuated in the absence of tPA/plasmin system. WT and tPA KO mice underwent sham or contusion injury followed by a single intraspinal injection of ChABC (50 U/ml) or Pen on day 14. An accelerating rotor rod was used to measure mice's motor balance on designated days and the maximum speed the mice remained on the machine was recorded. Two-way group comparisons are presented in graphs a–e with graphs a–c comparing differences due to genotype and time, while graphs d and e illustrate differences due to treatment and time. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA was used for multiple group comparisons. Significant ANOVA was followed by post hoc Holm–Sidak test. Brackets in c indicate significantly higher recovery in WT SCI+ChABC mice on day 18 compared with day 7 (p = 0.003) and day 10 (p = 0.004), and significantly higher recovery on day 21 compared with day 7 (p = 0.004). Asterisks in d indicate significantly higher recovery in WT SCI+ChABC mice compared with WT SCI+Pen group on day 18 (p < 0.001) and day 21 (p = 0.001). f, Motor coordination differences due to genotype and treatment were compared on day 21 (n = 3). A t test was used to compare between treatments and genotypes. Brackets with asterisks indicated significant difference between WT SCI+ChABC and WT SCI+Pen groups (p < 0.001) and WT SCI+ChABC and tPA KO SCI+ChABC groups (p = 0.02).