Figure 1.
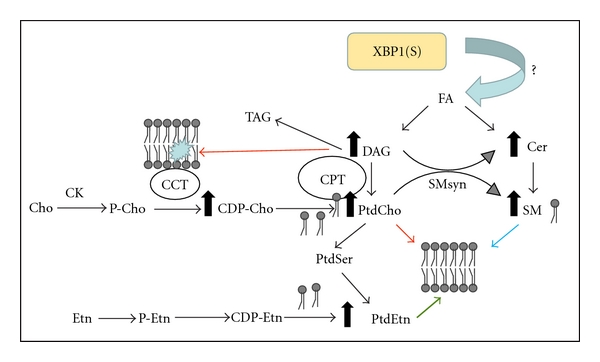
Activation of membrane phospholipid synthesis. Expression of XBP1(S) stimulates de novo fatty acid (FA) synthesis and the new FAs are incorporated into diacylglycerol (DAG) and ceramide (Cer), immediate precursors of phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), and sphingomyelin (SM) phospholipids, respectively. The mechanism of stimulation by XBP1(S) has not yet been defined. Elevation of the DAG level alters the membrane lipid composition which leads to activation of the choline cytidylyltransferase (CCT) enzymes which produce CDP-choline (CDP-Cho). The DAG and CDP-Cho precursors are converted to PtdCho by the choline phosphotransferase (CPT) enzymes. Excess DAG which is not incorporated into phospholipid, is redirected and incorporated into triacylglycerol (TAG) which can accumulate in lipid droplets. PtdCho conversion to SM is mediated by sphingomyelin synthase (SMsyn). PtdCho conversion to phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) is routed through phosphatidylserine (PtdSer). PtdEtn can also be synthesized from ethanolamine (Etn) and DAG by the alternative CDP-ethanolamine (CDP-Etn) pathway. Elevation of all three phospholipids, PtdCho, SM, and PtdEtn, contributes to membrane biogenesis during B cell activation. Cho, choline; P-Cho, phosphocholine; CK, choline kinase; Etn, ethanolamine; P-Etn, phosphoethanolamine.
