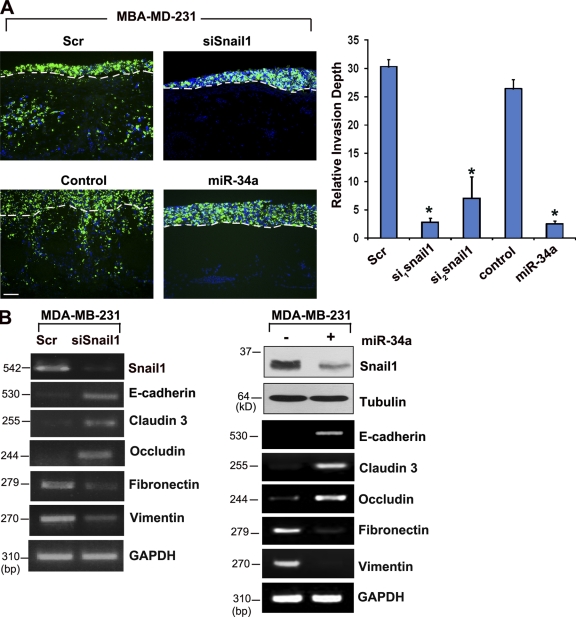
Figure 8.
Snail1- and miR-34- dependent invasion program of MDA-MB-231 cells. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with control siRNA (Scr), Snail1-specific siRNA (siSnail1), a control RNA oligonucleotide (control), or a miR-34a RNA oligonucleotide, and after a 24-h culture period in vitro, labeled with fluorescent nanobeads, and cultured atop the live chick chorioallantoic membrane for 3 d. Frozen sections were examined by fluorescence microscopy with labeled MDA-MB-231 cells colored green. The upper face of the chorioallantoic membrane is indicated by broken lines. Relative invasion depth was monitored after a 3-d assay period (n = 3; *, P ≤ 0.01). Error bars indicate mean ± 1 SD. Bar, 50 µm. (B) Snail1, E-cadherin, claudin 3, occludin, fibronectin, and vimentin mRNA transcript levels in MDA-MB-231 cells after transfection with control or Snail1 siRNAs, or control versus an miR-34a RNA oligonucleotide were determined by RT-PCR. Endogenous Snail1 protein levels were also assessed by immunoblot analysis after transfection with control (−) or miR-34a oligonucleotides (+) in MDA-MB-231 cells. Tubulin serves as the loading control. E-cadherin, claudin-3, occludin, fibronectin, and vimentin mRNA levels were determined in control or miR-34a–treated MDA-MB-231 cells by RT-PCR.