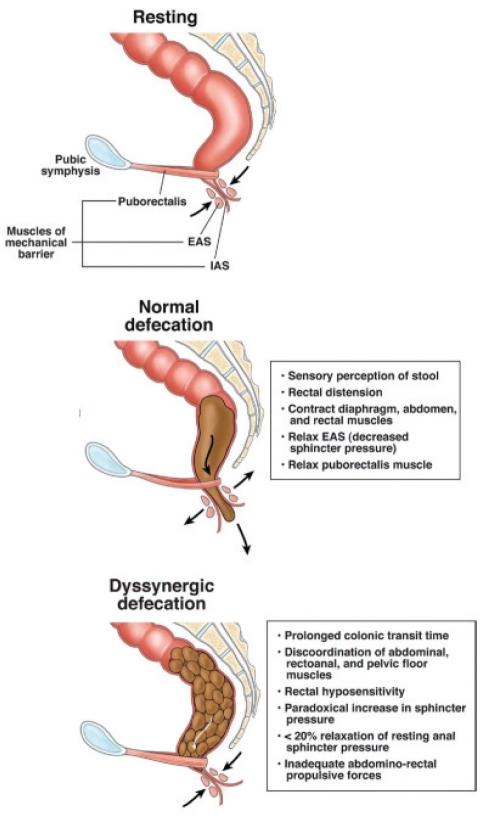
Figure 2).
Normal anatomy and physiology of the pelvic floor in the sagittal plane at rest, during normal defecation and during dyssynergic defecation. The resting profile shows the arrangement of the internal and external anal sphincters (IAS and EAS, respectively), as well as the puborectalis muscle. During defecation, the anal sphincters and the puborectalis relax and the abdominal and rectal contraction generate a push force to empty the rectum of stool. In patients with dyssynergia, the push effort or anal relaxation may be impaired, or the anal sphincters and puborectalis may not relax during attempted defecation, leading to incoordination (ie, dyssynergia) and stool retention. Adapted with permission from reference 10