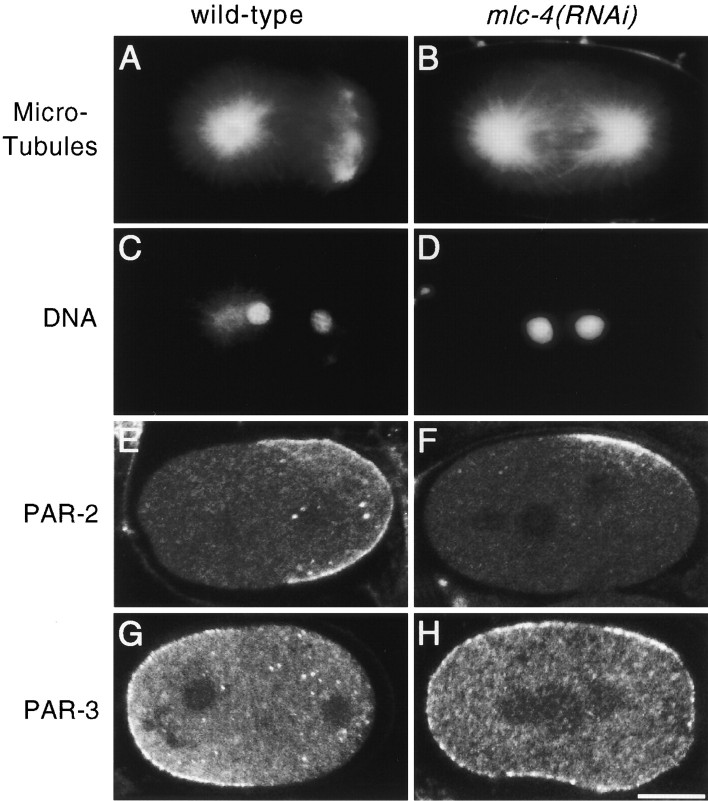
Figure 4.
First mitotic spindle morphology and PAR protein distribution in wild-type and mlc-4(RNAi) embryos. (A–D) Spindle morphology in wild-type and mlc-4(RNAi) embryos. (A and B) Spindle morphology at telophase of the first mitosis as visualized by immunolocalization with antibodies recognizing tubulin. A shows the morphology of wild-type spindle poles. The centrosome at the posterior pole splits and migrates well ahead of the anterior centrosome, giving a barlike morphology to the posterior spindle pole. B shows an mlc-4(RNAi) mutant embryo at the equivalent stage of the cell cycle. The morphology of both the anterior and posterior spindle poles resemble the anterior spindle pole in a wild-type embryo. (C and D) DAPI staining of the same embryos in A and B. Both embryos are in telophase of the first mitosis. (E–H) Distribution of PAR-2 and PAR-3 proteins in wild-type and mlc-4(RNAi) embryos. Images were obtained by confocal microscopy (see Materials and Methods). (E and F) Distribution of PAR-2. In the wild-type embryo (E), PAR-2 is localized to the posterior cortical hemisphere of the embryo. In the mlc-4(RNAi) mutant embryo (F), cortical PAR-2 is restricted to a small, laterally displaced, patch. (G and H) Distribution of PAR-3. PAR-3 is enriched in the cortex at the anterior of a wild-type embryo (G), but is uniformly distributed to the cortex in the mlc-4(RNAi) mutant embryo (H). Similar distributions of PAR proteins were seen in all mlc-4(RNAi) embryos at these early stages (5/5 for par-2, 7/7 for par-3). Bar, 10 μm.