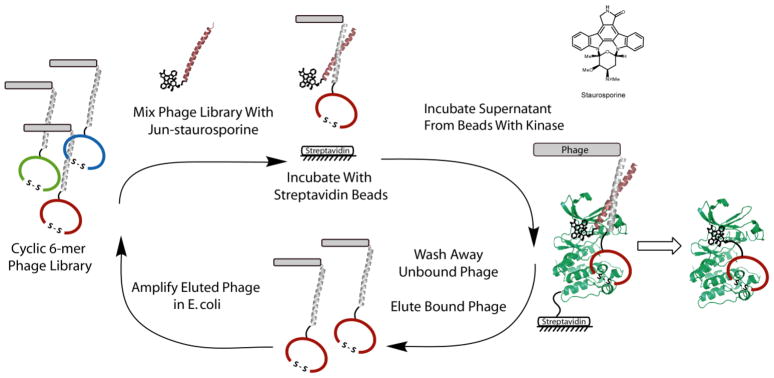
Figure 1. The Bivalent Selection Strategy Applied to Aurora A (AUR2).
Left The selection process is shown where the initial phage library (fos-cyclic peptides) is mixed with jun-staurosporine, incubated with “blank” streptavidin beads and then unbound phage/jun-staurosporine assemblies are transferred to AUR2 kinase streptavidin beads. Unbound phage are washed away after a 30-minute incubation period and the bound phage are eluted with low pH and amplified in E. coli. After this iterative process, selected peptides are identified by DNA sequencing and subsequently synthesized and tested by kinase assays. Right The general approach is outlined where the phage library and ATP-competitive compound are bound simultaneously via the non-covalent association of the leucine zipper pair, fos and jun. After an in vitro selection, peptides can be conjugated to the ATP-competitive compound, staurosporine, to generate a bivalent ligand.