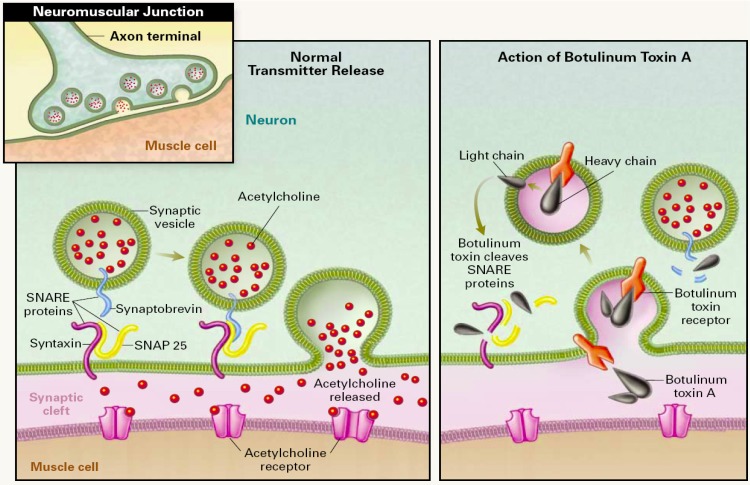
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of botulinum neurotoxin. Left side: Release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction is mediated by the assembly of the SNARE protein complex, allowing the the membrane of the synaptic vesicle containing acetylcholine to fuse with the neuronal cell membrane. SNARE protein complex includes synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin. Right Side: BoNT binds to the cell membrane and enters the neuron by endocytosis, the light chain is translocated through the membrane and then cleaves specific sites on the SNARE proteins, preventing complete assembly of the synaptic fusion complex and thereby blocking acetylcholine release. Botulinum toxins types B, D, F, and G cleave synaptobrevin; types A, C, and E cleave SNAP-25; and type C cleaves syntaxin. Reprinted with permission from [19]. Copyright © 2002 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved.