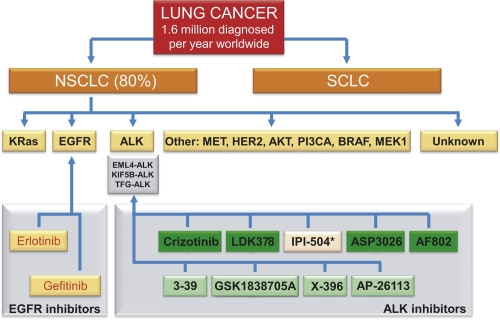
Figure 1. Schematic overview of potential tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Lung cancer is divided into two clinically important groups: NSCLC, which accounts for approximately 80% of lung cancer; and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). Within NSCLC, a number of ALK kinase inhibitors are shown in green, with the exception of IPI-504 (marked with an asterisk), which is an Hsp90 inhibitor. AKT; v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; BRAF, v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; EML, echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; KIF5B, kinesin family member 5B; KRas; v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; MEC1, mitosis entry checkpoint 1; MET, met proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor); PI3CA, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase catalytic subunit alpha; TFG, TRK-fused gene.