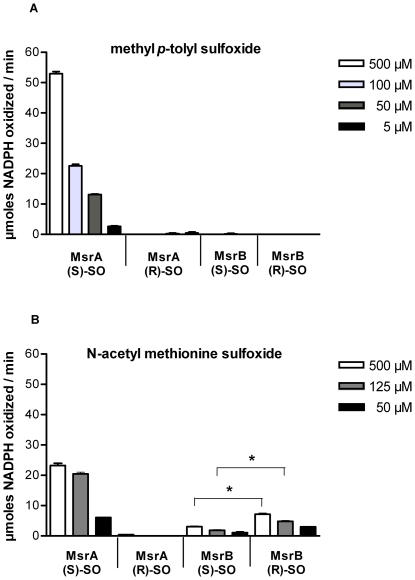
Figure 3. NADPH-linked reductase activity assay of recombinant MsrA and MsrB from S. Typhimurium.
A. The graph shows the amount of oxidized NADPH per minute for the reduction of 500, 100, 50 and 5 µM methyl p-tolyl sulfoxide by MsrA and MsrB, respectively. B. The graph shows the amount of oxidized NADPH per minute for the reduction 500, 125 and 50 µM N-acetyl methionine sulfoxide by MsrA and MsrB, respectively. The decrease of absorbance at 340 nm due to NADPH oxidation was measured in the presence of the S- or R-isomer of methyl p-tolyl sulfoxide (A), and in the presence of the S- or R-isomere of N-acetyl methionine sulfoxide (B) using purified His-tagged MsrA or MsrB. Besides 10 µM purified MsrA or MsrB, the test system contained 10 µM TrxR, 10 µM TrxB, 450 µM NADPH, and various concentrations of S- or R-methyl p-tolyl sulfoxide (Sigma), and N-acetyl methionine sulfoxide (MOLISA), respectively. Reactions were filled up to a final volume of 500 µl with a buffer containing 50 mM HEPES and 1 mM EDTA (pH 7.4). Reactions were carried out at 25°C and started after 10 min pre-incubation by addition of the oxidized methionine derivatives.