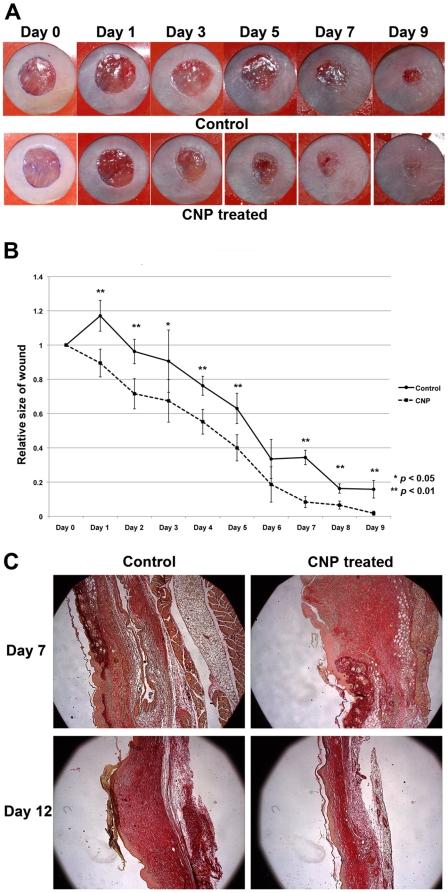
Figure 4. Intravenous injection of calcium-based nanoparticles accelerates healing of open mouse wounds.
(A) Representative photographs of mouse cutaneous wounds injected with calcium-based nanoparticle (CNP) suspension, or saline control. Differential healing was observed at all five time points checked (N = 5 for each time point). (B) Quantification of the wound area in nanoparticle-and control-treated wounds from days 0-9. The data is expressed as the mean ± SD. P-values were calculated using the Student's t-test (two-tailed). (C) Histologic sections representing the degree of collagen deposition in nanoparticle-treated vs. control wounds. Sections were taken from the center of wounds and stained with picrosirius red at post-injury days 7 and 12. Collagen deposition was qualitatively more rapid in nanoparticle-treated wounds.