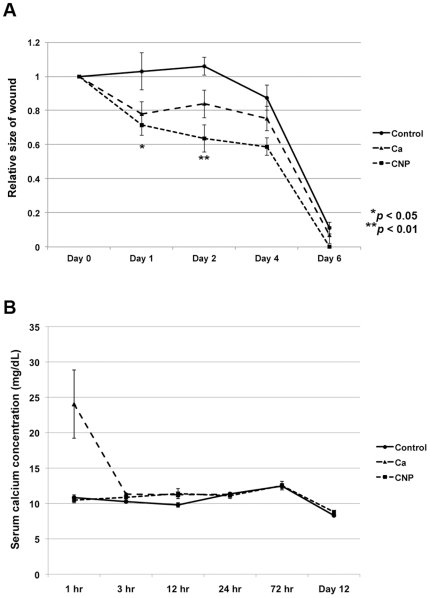
Figure 5. Intravenous injection of calcium chloride and calcium-based nanoparticles.
(A) Wounded mice received an injection of either calcium chloride, calcium-based nanoparticles (CNPs) or saline via the tail vein. The rate of wound healing was assessed after treatment in each group. Both calcium chloride and CNP-treatment accelerated wound healing relative to controls. CNP-treatment significantly decreased wound area compared to calcium chloride treatment by day 2 (N = 4 per group). P-values were calculated using the Dunnett's test. The data is expressed as the mean ± SD. (B) Serum calcium levels of mice were measured after they received an injection of calcium chloride, calcium-based nanoparticles or saline. Serum calcium levels remained unchanged after CNP injection, but were significantly increased 1 hour after CaCl2 injection.