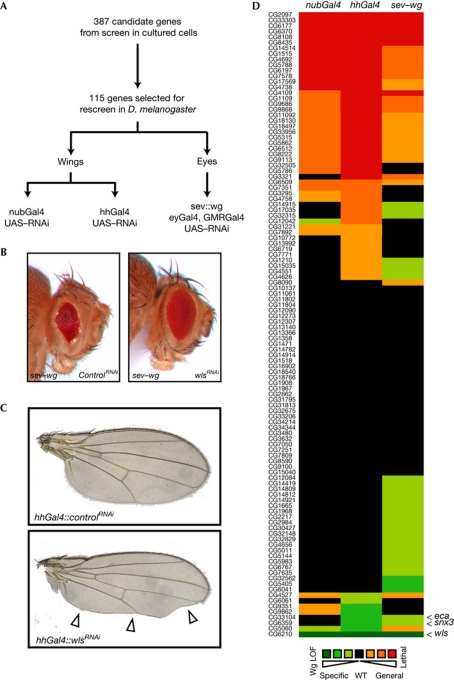
Figure 2.
Testing candidate genes for an effect on Wingless secretion in vivo. (A) Schematic illustration of the rescreening procedure. (B) Eyes of sev–wg-expressing flies coexpressing UAS–lacZ RNAi or UAS-wls RNAi induced by GMR–Gal4 and eyGal4. Inhibition of Wg secretion by reducing Wntless levels leads to a suppression of the sev–wg-induced rough-eye phenotype. (C) Wings of flies expressing UAS–lacZ RNAi or UAS–wls RNAi induced by hhGal4 in the posterior compartment of the developing wing. Strongly reduced Wg secretion caused by wls knockdown leads to loss of wing margin tissue (arrow heads). (D) Graphical summary of the results from the in vivo rescreen. For details, refer to supplementary Table S2 online. eca, éclair; hhGa14, hedgehog–Gal4; RNAi, RNA interference; nubGal4, nubbin–Gal4; sev, sevenless; snx3, sorting nexin 3; UAS, upstream activating sequence; LOF, loss of function; Wg, Wingless; wls, wntless; WT, wild type.