Figure 2.
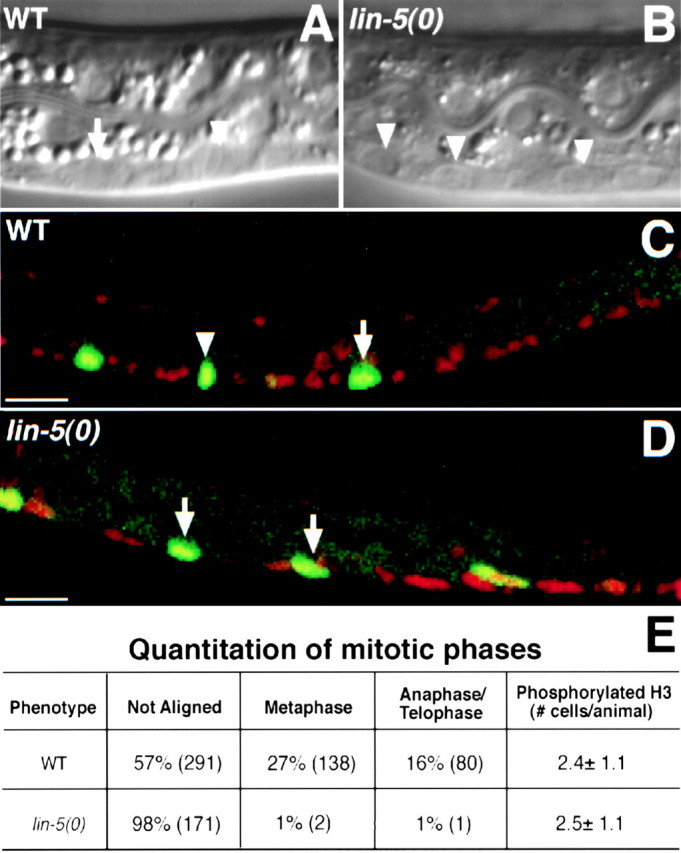
In lin-5 mutants, cells enter mitosis, chromosomes condense, but fail to align at the metaphase plate, and periodic activation and inactivation of Cdk1/NCC-1 continues. Synchronously growing L1 larvae were examined during the first round of (attempted) divisions of the ventral cord P cells. A and B, Nomarski microscopy images of living animals showing mitotic P cells at 9 h of postembryonic development. C and D, Epifluorescence images of animals of the same stage, but fixed and stained to visualize phosphorylated histone H3 (green) as a reporter of Cdk1/NCC-1 kinase activity, and counterstained with PI to reveal DNA (red). A, A wild-type animal in which three mitotic P cells are visible, one of which is in metaphase (arrowhead indicates metaphase plate) and one in early anaphase (arrow). B, A lin-5(0) mutant, showing three P cells that entered mitosis, but failed to align chromosomes at the metaphase plate. C, Example of a wild-type animal. Three mitotic P cells show phosphorylated histone H3 staining (green), one of which was in metaphase (arrowhead). D, Example of a lin-5(0) mutant with mitotic P cells that stained with the phosphorylated histone H3 antibody, but do not show metaphase or anaphase figures. E, Percentages of mitotic P cells with chromosomes that were unaligned, in metaphase alignment, or in anaphase, further demonstrate the lack of alignment and anaphase in lin-5(0) mutants. Numbers of P cells counted for each of the mitotic phases are indicated in parentheses. Equal numbers and similarly positioned P cells were found to contain phosphorylated histone H3 in wild-type and lin-5(0) mutant larvae, indicating continued activation, as well as inactivation, of NCC-1(Cdk1). Anterior is to the left, ventral is down. WT, Wild-type. Bars, 10 μm.
