Figure 4.
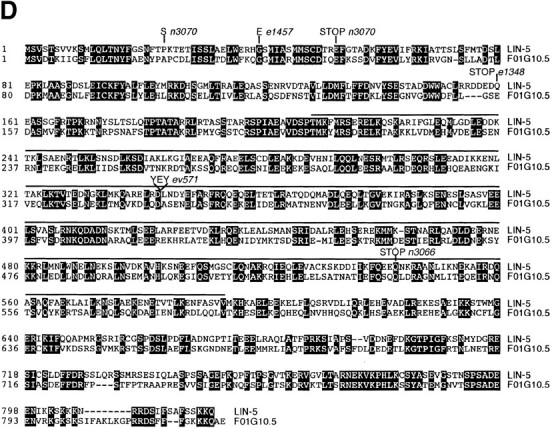
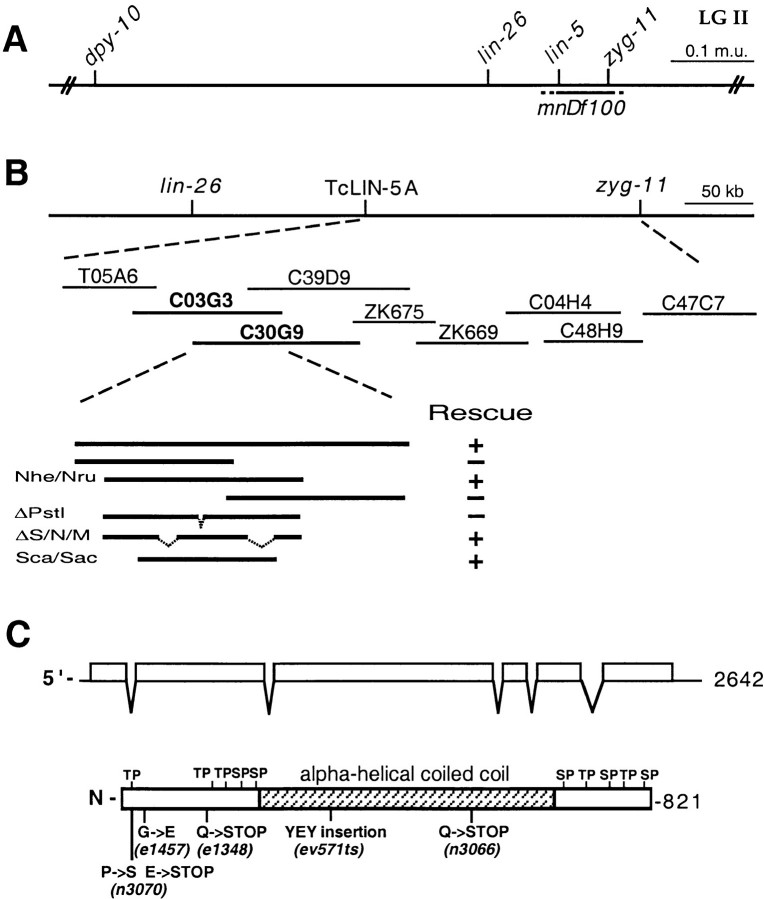
Molecular cloning of the lin-5 gene. A, Genetic map. The lin-5 region of linkage group II is indicated, as well as the closest cloned genes to the left and right of lin-5. Deletion mnDf100 includes the lin-5 gene. B, Physical map and cloning of lin-5 by germline transformation rescue. Cosmids are shown below the physical map. Overlapping cosmids C03G3 and C30G9 partially rescued the lin-5(0) phenotype, as described in Materials and Methods. The minimal rescuing fragment was predicted by the C. elegans Sequencing Consortium 1998 to contain three ORFs. Genomic fragments containing the second ORF partially rescued the lin-5(0) phenotype. C, The predicted lin-5 mRNA and LIN-5 protein. The predicted protein contains a large central α-helical coiled-coil domain, as well as ten potential phosphorylation sites for proline-directed kinases, such as Cdc2/Cdk1. D, LIN-5 amino acid sequence and alignment with the C. elegans predicted ORF F01G10.5. Black boxes indicate residues of identity. The overlined region indicates the predicted α-helical coiled-coil region shared between LIN-5 and F01G10.5. The molecular lesions in the lin-5 alleles are indicated below the predicted protein in C and above the lin-5 sequence in D.