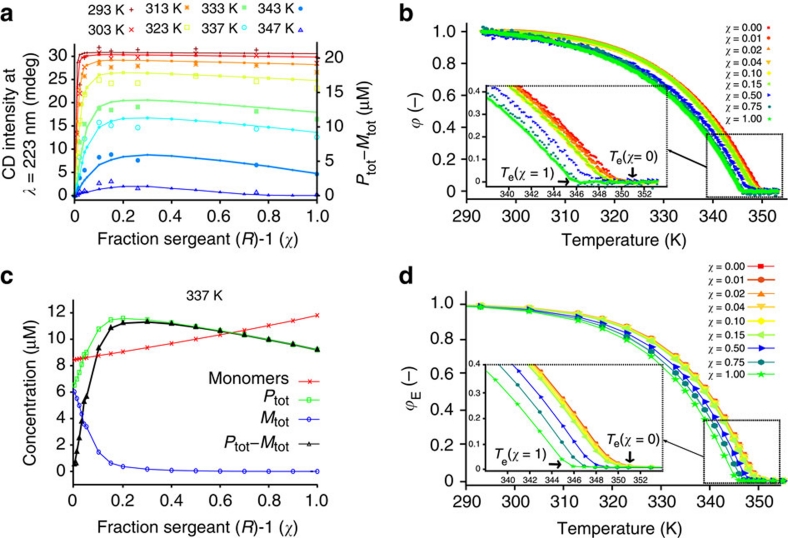
Figure 6. Sergeants-and-soldiers data and model results.
(a) CD intensity at λ=223 nm versus fraction of 'sergeant' (R)-1 (χ), for eight different temperatures at a total concentration of (R)-1+(A)-2 of 2.1×10−5 M in heptane. The large symbols represent the measured CD intensities at 223 nm while the small symbols connected by broken lines correspond to the excess helical sense, defined as the concentration difference of material present in P- and M-type supramolecular polymers, as calculated by the SSA. (b) Normalized degree of aggregation (ϕ) as a function of temperature27 obtained by UV–Vis spectroscopy for various mole fractions of 'sergeant' (R)-1. (c) Speciation plot at 337 K: total monomer concentration, concentration of BTA molecules belonging to P- and M-type supramolecular polymers and their difference (Ptot−Mtot) as a function of the mole fraction 'sergeant'. (d) Simulated normalized melting curves for various mole fractions of sergeant (R)-1. Due to the lower Te of pure (R)-1 supramolecular homopolymers compared with pure achiral supramolecular homopolymers, addition of aliquots of (R)-1 to a solution of (A)-2 results in a decrease of the Te of supramolecular heteropolymers consisting of (R)-1 and (A)-2. The fraction of aggregation at equilibrium, ϕE, is calculated as (ctot−[monomers])/ctot, where [monomers] represents the total concentration of chiral and achiral monomers.