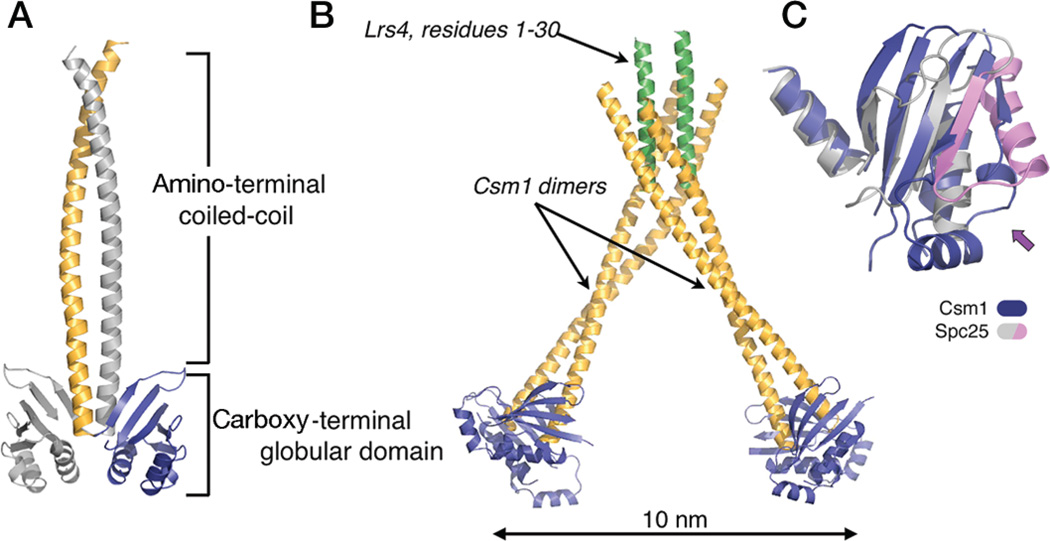
Figure 5.
Structure of the Csm1p/Lrs4p subcomplex of yeast monopolin. (A) Molecular organization of Csm1p. (B) Complex of Csm1p with Lrs4p. The amino-terminal 30 residues of Lrs4p form a dimerizing, α-helical segment; the dimeric segment, in turn, binds two Csm1p dimers, creating a V-shaped heterohexamer. The remaining residues of Lrs4p are disordered. (C) Superposition of the globular domains of Csm1p (blue) and Spc25p (magenta/gray). The arrow points to a lateral surface with somewhat divergent structures on the two proteins, as well as in Spc25p with respect to Spc24p (see Fig. 2C); this surface contains the hydrophobic patch, conserved among Csm1p orthologs, that binds Dsn1p (a component of the MIND complex) and Mif2p. (Figure from Corbett et al. 2010 and reprinted with permission from Cell Press © 2010.)