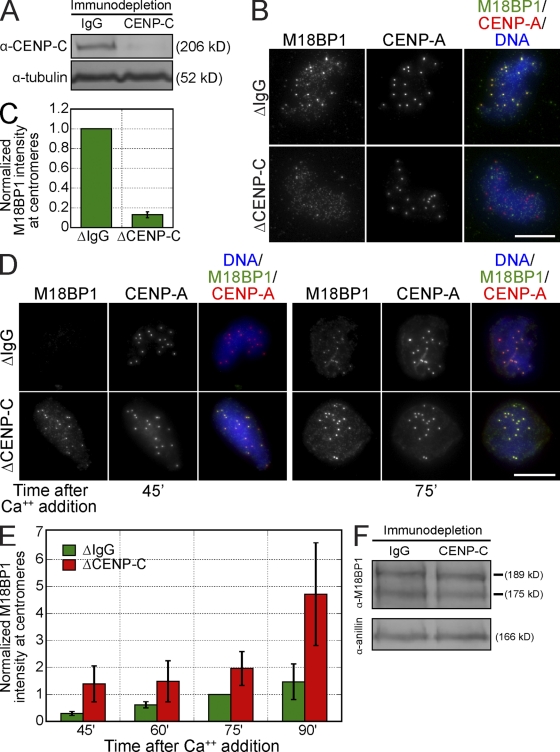
Figure 4.
CENP-C is required for M18BP1 assembly at metaphase centromeres in Xenopus egg extract. (A) Representative Western blot of mock- and CENP-C–depleted extracts. CENP-C depletion led to a >90% reduction in CENP-C levels. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) CENP-C depletion prevented M18BP1 assembly at centromeres in metaphase. Xenopus sperm chromatin was incubated in mock- or CENP-C–depleted metaphase extracts and stained for M18BP1 and CENP-A. The depletion conditions are listed to the left of the images, and immunolocalized proteins are listed above. (C) Quantification of M18BP1 fluorescence intensity at metaphase centromeres (normalized to the levels in mock-depleted extracts) after CENP-C depletion. Quantification was performed as described in Fig. 1. Error bars show SEM; n = 3. (D) CENP-C depletion led to premature, increased association of M18BP1 at interphase centromeres. Xenopus sperm chromatin was incubated in mock- or CENP-C–depleted extracts and stained for M18BP1 at various time points after release from metaphase arrest. Depletion conditions are listed to the left of the images, time (minutes) after calcium addition is listed below the images, and immunolocalized proteins are listed above. (E) Quantification of M18BP1 fluorescence intensity at centromeres in mock- and CENP-C–depleted extracts at various time points after release from metaphase arrest as described in D. Values are normalized to the levels in mock-depleted extracts 75 min after calcium addition. Quantification was performed as described in Fig. 1. Error bars show SEM; n = 3. (F) CENP-C depletion does not significantly affect M18BP1 levels in extract. Mock- and CENP-C–depleted extracts were Western blotted for M18BP1 and Anillin as a loading control. M18BP1-1 and M18BP1-2 levels in CENP-C–depleted extracts are 77 ± 8 and 92 ± 11% of control extracts, respectively (n = 3; error = SEM). Bars, 10 µm.