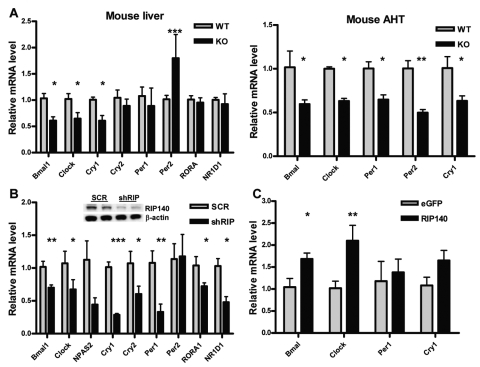
Figure 2.
RIP140 absence reduces the basal expression of clock genes. (A) mRNA level of different clock genes in the liver and anterior hypothalamus (AHT) of wild-type (WT) and RIP140 knockout (KO) mice. Samples were collected at ZT2 (2 hours after lights are turned on), and mRNA was extracted and quantified by RT-QPCR. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus control. Student t test (n = 6). (B) mRNA levels of clock genes in HepG2 human liver cell lines depleted of RIP140 quantified by RT-QPCR. RIP140 knockdown cells (shRIP) were generated by stably transfecting HepG2 cells with a vector expressing RIP140-specific shRNA. HepG2 cells constitutively expressing a nonspecific scrambled shRNA (scr) were used as a control. (Inset) Western blot showing RIP140 expression in the different cell lines. Bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus control. Student t test. (C) mRNA levels of clock genes in HuH7 human liver cells transiently transfected with a RIP140 expressing vector or equal amounts of an eGFP expressing vector. Bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 versus control. Student t test.