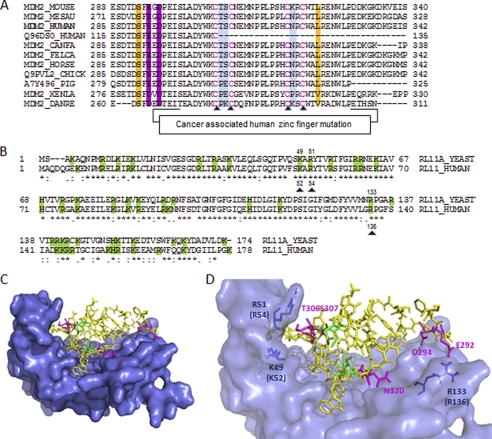
FIGURE 3.
RPL11 interaction with the zinc finger domain of MDM2 via hydrophilic residues. A, multiple sequence alignment of different MDM2 orthologs. Mutated residues for the binding experiments are highlighted in color. B, amino acid sequence comparison between yeast and human of RPL11s. Basic residues are shaded in green. Mutations made in human RPL11 are indicated by black triangles. The sequence alignment suggests that the basic residues in RPL11, which contribute to MDM2 binding, are highly conserved between yeast and human RPL11 orthologs. C, model of the MDM2-RPL11 complex with the zinc finger domain of MDM2 docked on the RPL11 structure. The model was constructed using the yeast RPL11 x-ray structure (PDB code 3O58, chain K7) and the NMR structure of the MDM2 zinc finger domain (PDB code 2C6A). RPL11 is represented as a molecular surface, and the zinc finger domain of MDM2 is shown as sticks. D, magnified view of C, showing the tight molecular interfaces between the zinc finger of MDM2 and the RPL11 basic canyon. The figures were made in PyMOL.