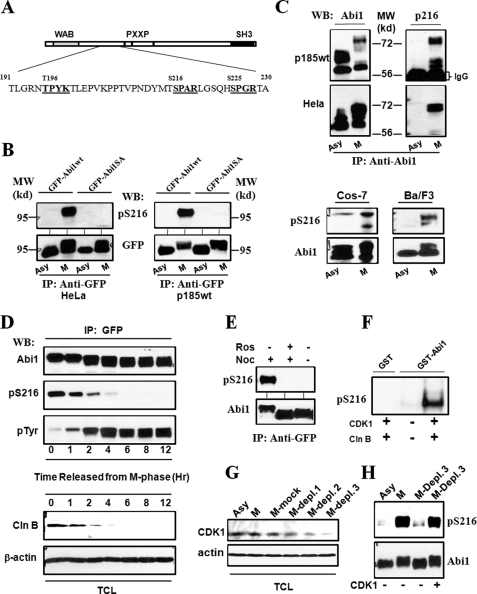
FIGURE 4.
Mitotic phosphorylation of Abi1 Ser-216 by CDK1. A, schematic representation of potential CDK1 phosphorylation sites in Abi1. The sequences that conform to consensus CDK1 phosphorylation motif ((S/T)PX(K/R)) are presented in bold. B, mitotic phosphorylation of the GFP-tagged Abi1 expressed in HeLa and p185wt cells. The HeLa (left panel) and p185wt (right panel) cells expressing GFP-Abi1 (GFP-Abi1wt) and GFP-Abi1S216A (GFP-Abi1SA) were treated with or without nocodazole for 16 and 12 h, respectively. The lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-GFP antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis using the specific antibody generated against Ser-216 phosphopeptide (anti-pSer-216) or anti-GFP antibody, as indicated. A 95-kilodalton molecular mass marker (MW) is indicated. C, mitotic phosphorylation of Ser-216 of endogenous Abi1 in Ba/F3, COS-7, HeLa, and p185wt cells. Upper panel, p185wt and HeLa cells, as indicated, were treated with or without nocodazole as described in B. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-Abi1 antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Abi1 (left panel) and anti-pSer-216 (right panel) antibodies. Lower panel, asynchronous (Asy) COS-7 and Ba/F3 cells as well as the COS-7 and Ba/F3 cells synchronized at M-phase (M), as described under “Experimental Procedures,” were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting for Ser-216 phosphorylation using anti-Abi1 and pSer-216 antibodies, as indicated. D, cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of Abi1 in p185wt cells. p185wt GFP-Abi1 cells were synchronized at M-phase by treatment with nocodazole (200 ng/ml) and okadaic acid (1 μm) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The cells were then washed three times with PBS and grown in normal growth medium for indicated time periods. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-GFP antibody. The immunoprecipitates and total cell lysates (TCL) were analyzed by Western blotting using indicated antibodies. Mitotic synchronization was confirmed by examining mitotic index of DAPI-stained cells and by Western blot analysis of the cell lysates using anti-phosphorylated histone H3 antibody as shown in supplemental Figs. S1 and S3, respectively. E, inhibition of Ser-216 phosphorylation by roscovitine. p185wt cells expressing GFP-Abi1 were treated with or without 200 ng/ml nocodazole (Noc) for 12 h in the presence or absence of 50 μm roscovitine (Ros). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blotting analysis using anti-Abi1 and anti-pSer-216 antibodies as indicated. F, in vitro phosphorylation of Ser-216 by CDK1/cyclin B. 5 μg of GST-Abi1, or GST as a control, were incubated with or without purified CDK1/cyclin B in an in vitro kinase reaction for 30 min. The GST fusion proteins were then subjected to Western blotting analysis using anti-pSer-216 antibody. G, depletion of CDK1 from the mitotic p185wt cell lysates. The lysates from the mitotic p185wt cells (M) were subjected to three rounds of immunoprecipitation with anti-CDK1 antibody (M-Depl. 1–3) or control IgG (M-mock). These lysates, together with the lysate from asynchronous p185wt cells, were then analyzed by Western blot using the indicated antibodies. H, aliquots of the GFP-Abi1 purified from interphase p185wt GFP-Abi1 cells were incubated with the asynchronous p185wt cell lysates or the mitotic p185wt cell lysates in which CDK1 was not depleted, or they were depleted by three rounds of immunoprecipitation (M-Depl. 3) as described in G. Ser-216 phosphorylation was examined by Western blot using anti-pSer-216 antibody. The blot was then stripped and reprobed with anti-Abi1 antibody to confirm that an equal amount of GFP-Abi1 was used.