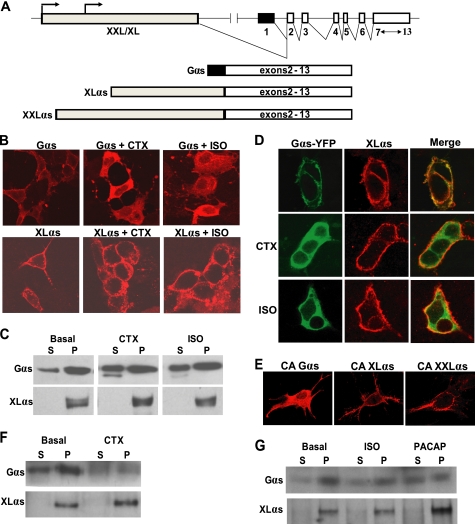
FIGURE 1.
XLαs is targeted differently from wild-type Gαs upon activation. A, depiction of the GNAS locus and the transcripts encoding Gαs, XLαs, and XXLαs. Exons and introns are indicated by boxes and connecting lines, respectively. Splicing pattern is shown by angled lines. Arrows indicate the origin of transcription. B and C, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with cDNA encoding either HA-tagged Gαs or XLαs. Forty eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with 10−5 m isoproterenol for 20 min or with 1 μg/ml CTX for 4 h, and subcellular localizations of Gαs and XLαs were examined by immunocytochemical analysis by using the anti-HA antibody (B), and Western blot analysis by using either the anti-HA antibody or a polyclonal antibody against the common C terminus of Gαs and XLαs. (C). D, HEK293 cells were transiently co-transfected with cDNA encoding HA-tagged XLαs and Gαs-YFP. Forty eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with 10−5 m isoproterenol (ISO) for 20 min or with 1 μg/ml CTX for 4 h. XLαs and Gαs-YFP were detected in the same cells by immunocytochemical analysis using the anti-HA antibody and by confocal fluorescence microscopy. E, GnasE2−/E2− cells were transiently transfected with cDNA encoding HA-tagged Gαs-R201H, XLαs-R543H, or XXLαs-R844H. Two days later, immunofluorescence confocal microscopy using anti-HA antibody was employed to determine the subcellular localization of those mutants. F and G, subcellular localizations of endogenous Gαs and XLαs in PC12 cells stimulated by 1 μg/ml CTX (F), 10 μm isoproterenol (ISO; G), or 100 μm PACAP (G). Endogenous Gαs and XLαs in soluble (S) and particulate (P) fractions were subjected to immunoblotting with the polyclonal antibody against Gαs and XLαs.