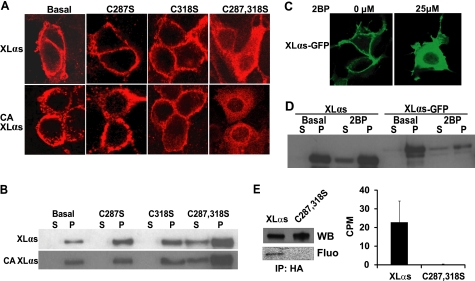
FIGURE 4.
Substitution of conserved cysteine residues in the XL domain and inhibition of protein palmitoylation disrupts plasma membrane targeting of XLαs at steady state. A, immunocytochemical analysis of subcellular distribution for wild-type and Cys-to-Ser mutants of XLαs in HEK293 cells by using the anti-HA antibody. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with expression constructs encoding HA-tagged wild-type or Cys-to-Ser mutants of XLαs (Cys-287 and Cys-318). Forty eight hours after transfection, subcellular localizations of these XLαs mutants were investigated. CA, GTPase deficient, constitutively active form analogous to R201H. B, Western blots using the anti-Gαs and -XLαs C-terminal antibody was performed for determining the subcellular localizations of Cys-to-Ser mutants of XLαs in transfected HEK293 cells. C287S,C318S (C287,318S). C, subcellular localization of XLαs-GFP transiently expressed in HEK293 cells treated with either the vehicle or 25 μm 2BP immediately after transfection. D, Western blot analysis (anti-Gαs C-terminal antibody) of HEK293 cell lysates transiently expressing native XLαs or XLαs-GFP. Cells were treated with either the vehicle or 25 μm 2BP immediately after transfection. S, soluble fraction; P, particulate fraction. E, palmitoylation of XLαs, but not the XLαs-C287S,C318S mutant, transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. Following metabolic labeling with [3H]palmitic acid, transfected cells were lysed, and the HA-tagged recombinant proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed either by Western blot (WB) analysis using the anti-Gαs C-terminal antibody or by fluorography (Fluo), for which the exposure time was at least 6 weeks (representative of two independent experiments). In some experiments, gel slices corresponding to the immunoreactivity of XLαs and the mutant were counted to determine palmitoylation (right). Data are counts per min (CPM) above the background and represent mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments.