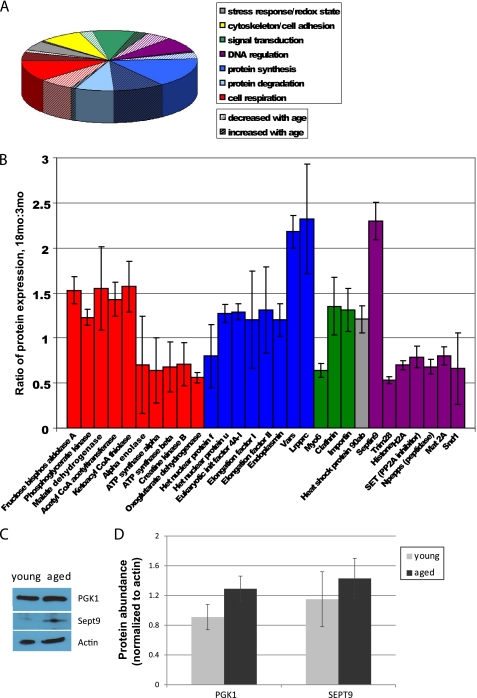
FIGURE 3.
Comparative proteomics assay reveals age-related changes in metabolic protein expression. A, 124 proteins were identified by MS/MS and grouped by pathway. B, identified proteins with significant age-related differences are shown (error bars, S.D.). Few changes were observed in proteins involved in cytoskeletal maintenance, cell-cell adhesion, stress response, redox state, or protein degradation. Significant age-related decreases were observed primarily in signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, and aerobic respiration (ATP synthesis), whereas significant age-related increases in protein expression were observed primarily in signal transduction, protein synthesis, and anaerobic respiration. C, Western blot analyses were performed to measure the abundance of several proteins identified using MS/MS, including phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK1) and septin 9 (Sept9). D, a 41% increase in phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and a 25% increase in septin 9 were observed, although these changes were not statistically significant (p > 0.05; error bars, S.E.).