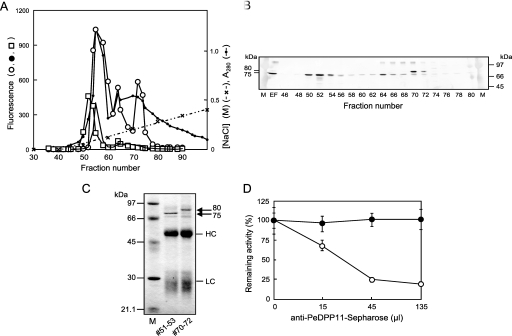
FIGURE 3.
Detection and identification of native PeDPP11 separated by DEAE-Sephacel anion-exchange chromatography. A, a soluble extracellular fraction from P. endodontalis was separated using DEAE-Sephacel chromatography with a 0–0.6 m linear gradient of NaCl in buffer A, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Hydrolysis of KA (open circle)-, suc-AAA (closed circle)-, and ac-DNLD-MCA (square) of even fractions (10 μl) was measured. B, proteins at fractions 46–80 (even numbers) were separated on SDS-PAGE, then subjected to immunoblotting with anti-PeDPP11 serum (105-diluted). EF, extracellular fraction (10 μl). M, rainbow marker. C, fractions 51–53 and 70–72 (3 ml each) were immunoadsorbed to the PeDPP11 antibody resin, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Proteins bound to the resin were extracted with SDS-sample buffer, separated on SDS-PAGE, and subjected to N-terminal sequencing. LC and HC, light and heavy chains, respectively, of immunoglobulins. D, fraction 52 or 56 (100 μl) of DEAE-chromatography (panel A) was incubated with 15, 45, or 135 μl of a 50% suspension of a PeDPP11-antibody resin. After rotation at 0 °C for 8 h, samples were centrifuged, and the remaining activity in the supernatant was determined with ac-DNLD-MCA for the sample from fraction 52 (open circle) and suc-AAA-MCA from fraction 56 (closed circle). Values are expressed as percent (mean ± S.D., n = 3) of the control incubated with Sepharose 4B. M, molecular mass markers.