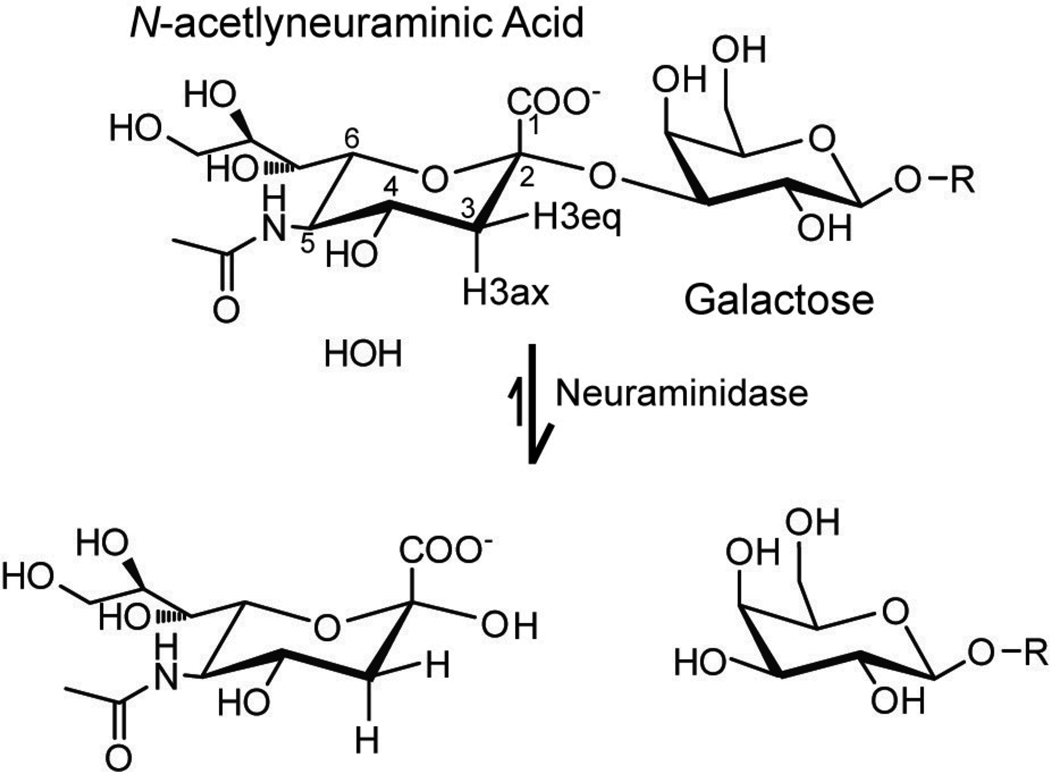
Figure 1.
The most common sialic acid found on human cells is N-acetylneuraminic acid, which is shown with an α2–3 linkage to a β-galactosyl residue. This linkage is hydrolyzed by the enzyme neuraminidase to liberate the N-acetylneuraminic acid. Note the axial and equatorial hydrogen atoms in the top structure.