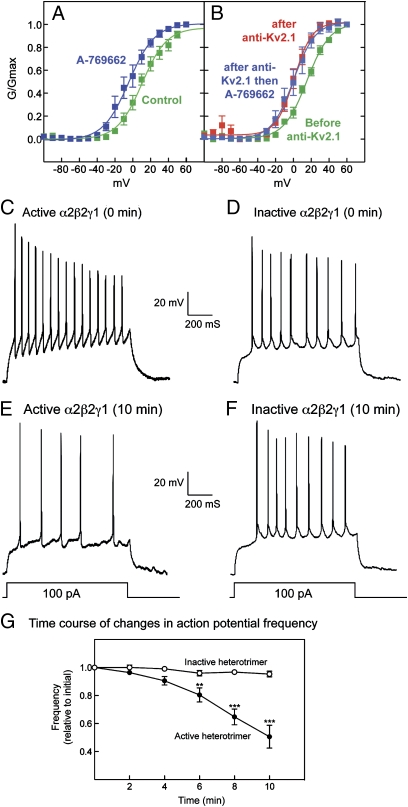
Fig. 5.
Effect of AMPK on K+ conductance and action potentials in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. (A) Voltage–conductance plot showing effects of A-769662 on the isolated K+ delayed rectifier current in native hippocampal neurons. (B) Voltage–conductance plot for the K+ delayed rectifier component in hippocampal neurons before/after intracellular dialysis of Kv2.1 antibody (anti-Kv2.1) and after subsequent application of A-769662. Individual data points are mean ± SEM (n = 5). Results were fitted to the sigmoidal Boltzmann equation, and the curves were generated using the parameters shown in Table S6. (C–F) Sample recordings from two cells at time 0 (C and D) and after intracellular dialysis for 10 min (E and F) of either active (C and E) or inactive (D and F) AMPK. (G) Action potential frequency (mean ± SEM of changes in individual cells over 10 min; n = 7; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Dunnett's multiple comparison test). The mean initial frequencies of the cells injected with the active and inactive heterotrimers were 47 ± 7 and 41 ± 7 Hz, respectively.