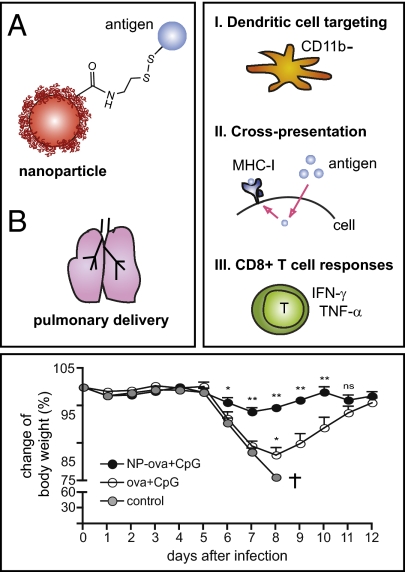
Fig. P1.
Antigen conjugation to nanoparticles and pulmonary delivery induce specific targeting of the antigen to DCs, cross-presentation, and robust cellular immune responses. The model antigen ovalbumin was covalently conjugated to the surface of 30-nm nanoparticles via a disulfide bond (A). Administration of this antigen–nanoparticle conjugate together with the adjuvant molecule CpG to the mouse lung (B) influenced antigen uptake by lung DCs and trafficking to the draining lymph node (Upper Right, I), and promoted antigen cross-presentation in vitro and in vivo (Upper Right, II). Accordingly, potent CD8+ T-cell responses were induced (Upper Right, III). Mice vaccinated with nanoparticle-conjugated ovalbumin and CpG (NP-ova+CpG) were protected from morbidity following infection with a recombinant influenza virus expressing the ovalbumin CD8+ T-cell epitope (Lower).