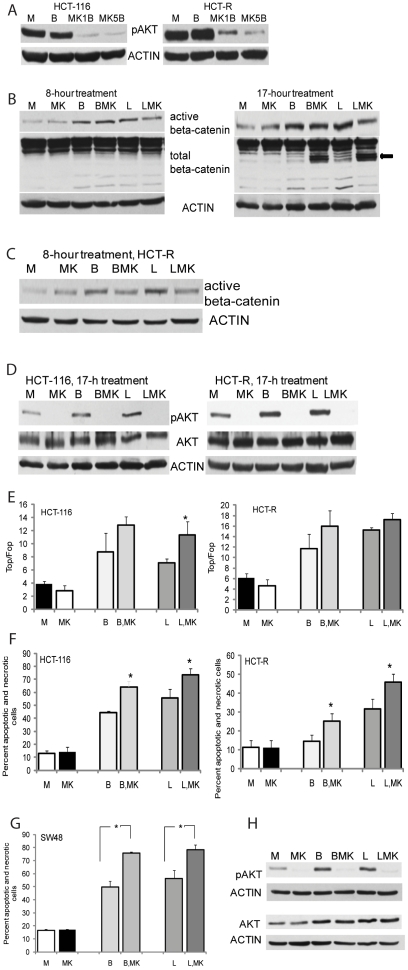
Figure 3. Simultaneous increase in canonical Wnt signaling and suppression of pAKT result in increased apoptosis of CC cells.
(A) Suppression of pAKT levels in CC cells by the allosteric inhibitor MK2206. Representative western blot analysis of CC cells exposed for 17 hrs to mock (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), butyrate and 1 µM MK2206 (MK1B), or butyrate and 5 µM MK2206 (MK5B). (B) The steady-state levels of transcriptionally active beta-catenin are not decreased in HCT-116 cells by combined treatment with a HDACi and MK2206. Cells were exposed for 8 or 17 hrs to mock treatment (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), butyrate and 5 µM MK2206 (BMK), 100 nm LBH589 (L), or 100 nm LBH589 and 5 µM MK2206 (LMK). Total cell lysates were analyzed for steady-state levels of total and Ser37/Thr41 dephosphorylated beta-catenin. Representative western blot analysis is shown. (C) Active beta-catenin levels in HCT-R cells exposed for 8 hrs to mock (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), butyrate and 5 µM MK2206 (BMK), 100 nm LBH589 (L), or 100 nm LBH589 and 5 µM MK2206 (LMK). (D) Representative western blot analysis of Ser473-phosphorylated AKT (pAKT) and total AKT (AKT) levels in CC cells exposed for 17 hrs to mock (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), butyrate and 5 µM MK2206 (BMK), 100 nm LBH589 (L), or 100 nm LBH589 and 5 µM MK2206 (LMK). (E) The induction of Wnt/catenin-dependent transcriptional activity (TopFlash/FopFlash) in CC cells by a HDACi (butyrate or LBH589) is not suppressed by a pAKT inhibitor. Cells were nucleofected at one million with 1 µg of plasmid (TopFlash or FopFlash) and pRL-TK, diluted, and plated at 30,500 cells per well in 96-well plates. At 24 hrs post-nucleofection, cells were treated for 8 hrs with mock (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), butyrate and 5 µM MK2206 (BMK), 100 nm LBH589 (L), or 100 nm LBH589 and 5 µM MK2206 (LMK). Data represent the mean from results of at least three experiments. Statistically significant differences are noted by a star. (F) Apoptotic levels in HCT-116 and HCT-R cells exposed to HDACis and a pAKT inhibitor. The cells were exposed for 28 hrs to: mock treatment (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), butyrate and 5 µM MK2206 (BMK), 100 nm LBH589 (L), or 100 nm LBH589 and 5 µM MK2206 (LMK). Percent apoptosis and necrosis was calculated by dividing the number of apoptotic and necrotic cells by the total number of analyzed cells. Each experiment had triplicate samples per treatment; data represent the mean of three experiments. Statistically significant differences are noted by a star. (G, H) SW48 human CC cells with wild type KRAS are as sensitive as HCT-116 cells with mutant KRAS to the combined treatment with a HDACi and a pAKT inhibitor. SW48 cells were treated and analyzed as described in Figs.3D and 3F. Representative western blots and apoptotic data, representing the mean of three experiments, are shown. Statistically significant differences are noted by a star.