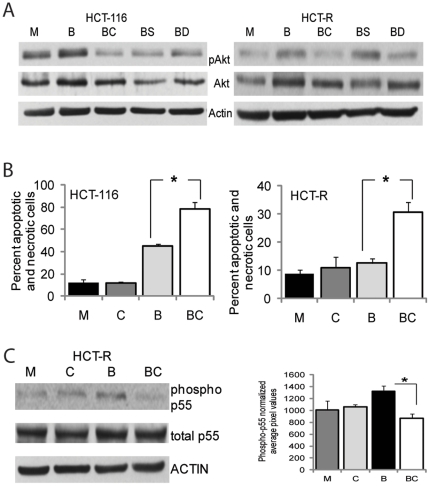
Figure 4. Diet-derived pAKT inhibitors mimic the effects of MK2206 in augmenting HDACi-induced apoptosis in CC cells.
(A) Diet-derived compounds suppress butyrate-induced pAKT levels in CC cells. Representative western blot of cells exposed for 14 hrs to mock treatment (M), 5 mM butyrate (B), 5 mM butyrate and 4 µg/ml CAPE (BC), 5 mM butyrate and 20 µM sulforaphane (BS), 5 mM butyrate and 40 µM DATS (BD). Detection of pAKT, total AKT (AKT), and ACTIN was carried out with total cells lysates. (B) Apoptotic levels in HCT-116 and HCT-R cells exposed for 28 hrs to mock treatment (M), 4 µg/ml CAPE (C), 5 mM butyrate (B), or butyrate and 4 µg/ml CAPE (BC). Apoptotic assays were performed by flow cytometry. Percent apoptosis and necrosis was calculated by dividing the number of apoptotic and necrotic cells by the total number of analyzed cells. Each experiment had triplicate samples per treatment; data represent the mean of three experiments. Statistically significant differences (P<0.05) are noted by a star. (C) CAPE suppresses the phospho-p55 PI3K levels in butyrate-treated HCT-R cells. Cells were treated as in (B) for 17 hrs, and total cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting. Phospho-p85 levels were not detected; however, phospho-p55 levels were detected and the bar graph next to the western blot represents the densitometry quantification of phospho-p55 PI3K in three independent experiments.