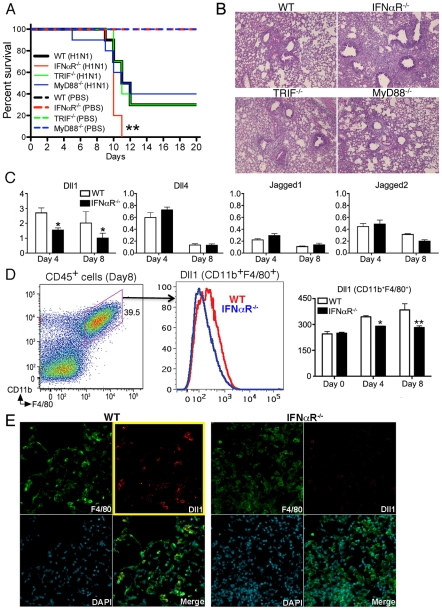
Figure 4. IFNαR.
−/− mice showed higher mortality with impaired Dll1 expression during influenza virus infection. (A) Survival rate in WT (black), IFNαR−/− (red), TRIF−/− (green), and MyD88−/− (blue) mice. Mice were inoculated intranasally with PBS (dotted line) or H1N1 at 1×104 PFU (solid line) per each group of mice. Results are expressed as the percentage of survival from 10 individual mice per group. **P<0.01 compared with WT mice (B) Histological appearance of lungs from WT, IFNαR−/−, TRIF−/−, MyD88−/− mice at 8 days post-infection of influenza virus (C) Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to measure the transcript levels of Notch ligands at Day 4 and Day 8 after inoculation of influenza virus. *P<0.05 compared with WT mice (D) The level of Dll1 in lung macrophages (CD11b+F4/80+) from WT or IFNαR−/− mice was determined by flow cytometry at Day 4 and Day 8 after inoculation of influenza virus. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with WT mice. (E) Confocal immunofluorescent examination of influenza infected lungs at 8 days post-infection, Dll1+ cells (red) merged with F4/80+ cells (green) in WT and IFNαR−/− mice. Blue staining indicates DAPI. Original magnification,×200. Shown are representative sections from 1 mouse of 4 per group. Data shown indicate mean ± SEM and are from a representative experiment of 3 independent experiments. Each time point represents at least 4 mice per group.