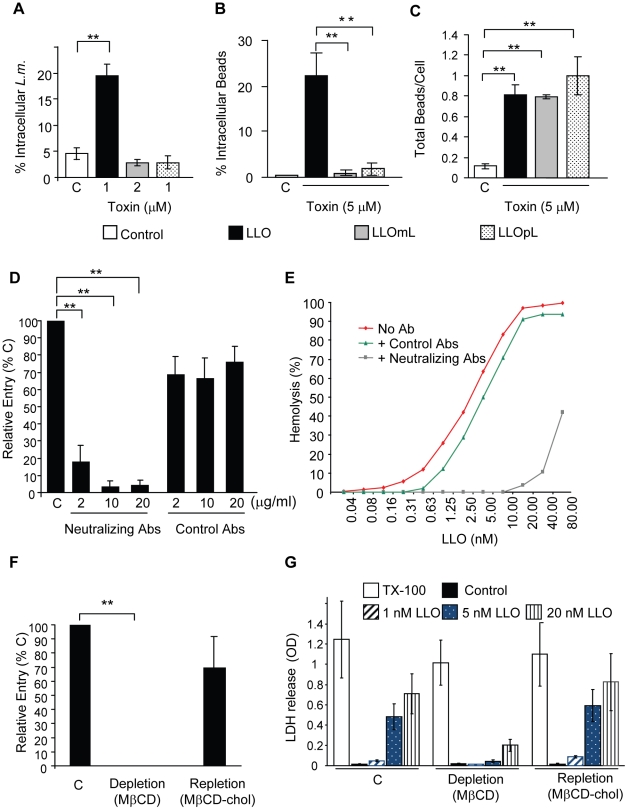
Figure 7. Formation of pore complexes is required for efficient bacterial and bead entry into HepG2 cells.
(A) LLO-deficient L. monocytogenes (Δhly, L.m.) were treated with coating buffer in the absence (white bars, C), or presence of LLO, LLOmL, or LLOpL. Cells were infected at 37°C for 30 min (MOI = 20). Samples were washed, fixed, and fluorescently labeled to enumerate bacterial entry by fluorescence microscopy. Results were the mean ± SEM (n≥3). (B) and (C) HepG2 cells were incubated with BSA- (Control; C) or BSA/toxin (LLO, LLOmL, or LLOpL)-coated beads for 30 min at 37°C (MOI = 20). Cells were washed, fixed, and labeled to enumerate bead entry (B) and association (C) by fluorescence microscopy. Results were the mean ± SEM (n≥3). (D) HepG2 cells were incubated with BSA/LLO-coated beads for 30 min at 37°C, in the presence or absence (C) of LLO-neutralizing or control antibodies. Cells were washed, fixed, and fluorescently labeled. Bead entry was measured by fluorescence microscopy and the results, mean ± SEM (n≥3) were expressed relative to the control (C). (E) Representative LLO hemolytic curves in the presence or absence (No Ab) of the neutralizing or control antibodies (10 µg/ml) were performed at pH 7.4, 37°C. (F) Control (C), cholesterol-depleted and -repleted HepG2 cells were incubated with BSA/LLO-coated beads for 30 min at 37°C. Bead entry was measured by fluorescence microscopy and the results, mean ± SEM (n≥3) were expressed relative to the control. (G) Control (C), cholesterol-depleted and -repleted HepG2 cells were incubated with various concentrations of LLO, 0.2% TX-100, or MEM (Control) at 37°C for 30 min. LDH release was measured using the TOX7 assay kit. Results are the mean ± SEM (n≥3).