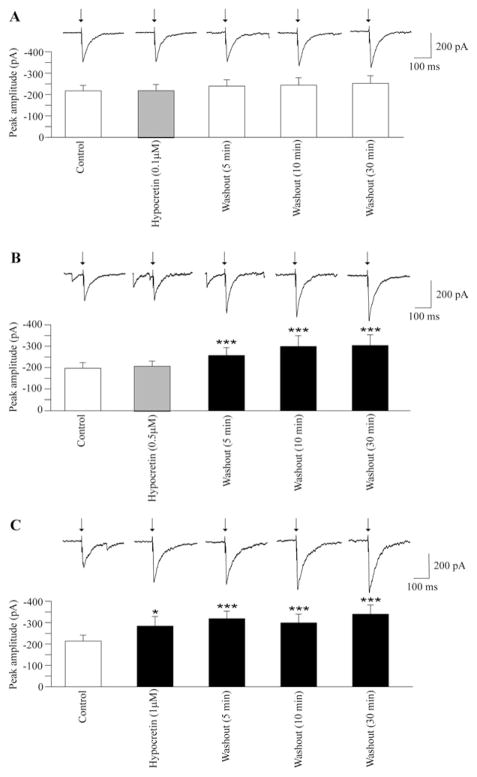
Fig. 1.
Stimulation of the LPGi evoked a GABAeric pathway and activation of postsynaptic GABA receptors in cardiac vagal neurons (A, B, C). Application of hypocretin-1 at a concentration of 0.1 μM did not alter the evoked GABAergic current as shown in a typical example (A, top) and in the summary data from nine neurons (A, bottom). Similarly, application of hypocretin-1 at a concentration of 0.5 μM did not change GABAergic current evoked by stimulation of the LPGi. However, during washout of hypocretin-1 (0.5 μM) the LPGi-evoked GABAergic current was significantly increased up to 30 min (a typical example is shown in B, top, and the summary data from nine neurons are illustrated in B, bottom). As shown in C, application of hypocretin-1 at a concentration of 1 μM significantly increased GABAergic current evoked by LPGi stimulation and the evoked GABAergic current remained elevated during the washout period up to 30 min (C, top, typical experiment, and C, bottom, summary data from nine neurons). In this and all subsequent figures: arrow indicates electrical stimulation. ■ with asterisks indicates statistically significant differences * P<0.05 and *** P<0.001.