Figure 2. iTBS and cTBS induced changes in EEG gamma power and spontaneous multi-unit spiking activity (MUA).
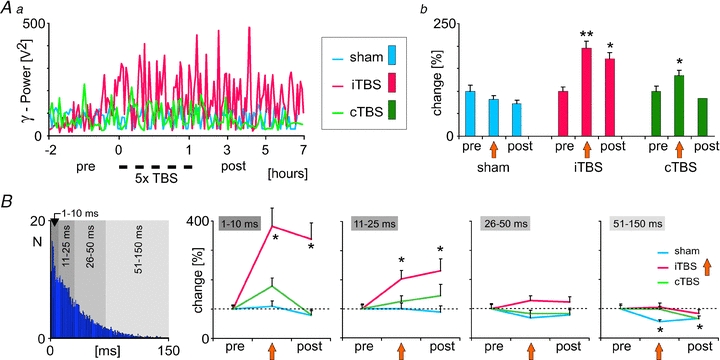
iTBS but not cTBS caused a lasting increase in the gamma power of the EEG recorded from frontal cortical areas in the anesthetized rat (Aa and b), which was accompanied by changes in spontaneous spiking activity recorded from layer IV of rat somatosensory cortex. B, increase in the rate of MUA following iTBS (not explicitly shown here, see Benali et al. 2011) was characterized by a stronger increase in short inter-spike intervals (1–10 and 11–25 ms), while longer intervals (>25 ms) were less changed. The left-most diagram shows a typical, Poisson-like, inter-spike interval distribution of cortical MUA. Results diagrams taken and rearranged from Benali et al. (2011), with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
